Civil Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
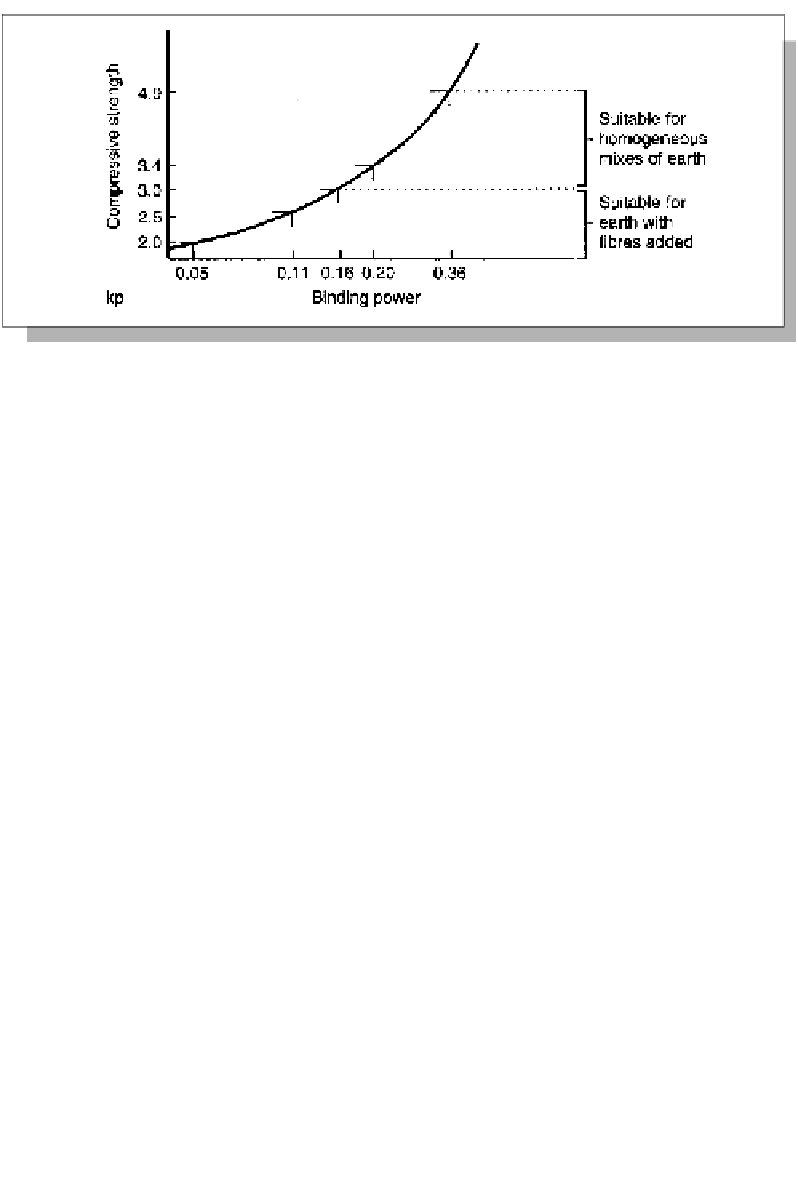
Figure 8.6: Determining compressive strength (according to DIN 18952). The properties of the
earth can be read on the right.
a naturally high moisture content will shrink considerably during drying. To
assess the moisture content of the earth, a sample of it is weighed, dried out,
then re-weighed. The moisture content is the equivalent of the difference
between the two weights.
Generally speaking, earth with a high moisture/clay content is best used for
an air-dried earth block. Most of the shrinkage will have taken place before the
blocks are laid. Through adding plenty of natural fibres, an earth rich in clay can
be used for ramming as in the pisé technique.
The preparation of earth
Once the earth has been selected according to the above methods, the topsoil is
removed to a depth of 20-30 cm. The earth uncovered is then sieved through a
steel net with holes 2.4 cm in size for ramming earth, or 1 cm for the production
of earth and clay blocks. If the earth and clay mixture has a variable moisture con-
tent, it must be well mixed and stored under a tarpaulin for three to four weeks.
Where necessary, stabilizers or extra amounts of sand or clay can be added
either during sieving of the earth or later with an earth grinder. Mixtures con-
taining cement and lime must be used immediately. Others can be stored, but
they must be covered with a tarpaulin to preserve the moisture.
Earth structures
Earth is transported straight to the building site without any industrial treat-
ment. Here it is put into casts to make blocks or rammed between shuttering to
make walls.