Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
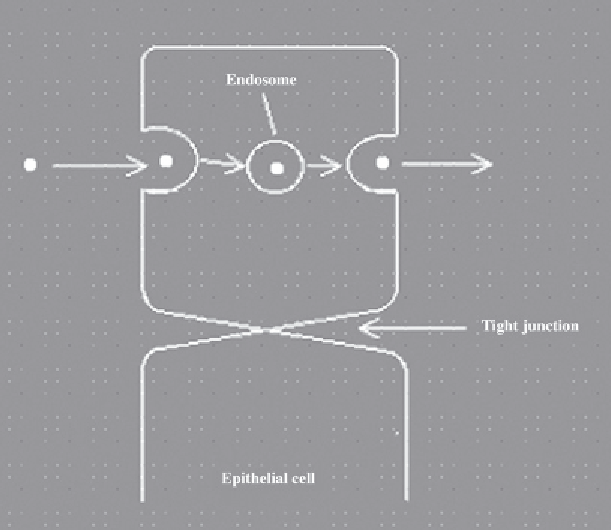
Figure 4.6
Likely mechanisms by which macromolecules cross cellular barriers in order to reach the blood-
stream from (in this case) the lung. Transcytosis entails direct uptake of the macromolecule at one surface
via endocytosis, travel of the endosome vesicle across the cell, with subsequent release on the opposite cell
face via exocytosis. Paracellular transport entails the passage of the macromolecules through 'leaky' tight
junctions found between some cells
4.10.3 Nasal, transmucosal and transdermal delivery systems
A nasal-based biopharmaceutical delivery route is considered potentially attractive as:
•
it is easily accessible;
•
nasal cavities are serviced by a high density of blood vessels;
•
nasal microvilli generate a large potential absorption surface area;
•
nasal delivery ensures the drug bypasses fi rst-pass metabolism.
However, the route does display some disadvantages, including:
•
clearance of a proportion of administered drug occurs due to its deposition upon the nasal mu-
cous blanket, which is constantly cleared by ciliary action;
Search WWH ::

Custom Search