Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
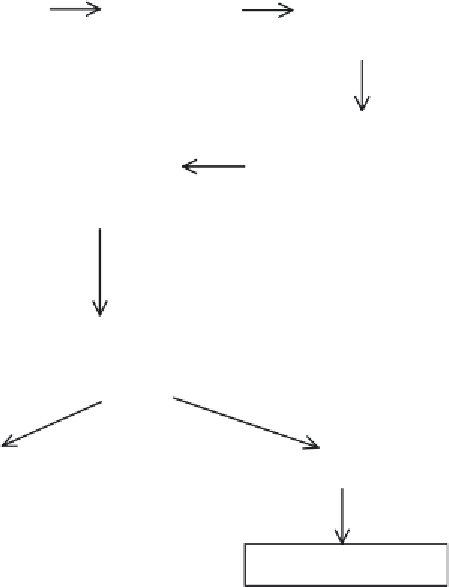
Immunize
large animal
(e.g. horse)
Collect
antibody-containing
antiserum/plasma
Initial purification
(precipitation)
High resolution
chromatographic
purification (e.g.
ion-exchange)
Addition of
stabilizers,
preservatives and
adjustment of potency
Sterile filtration and
aseptic filling
Liquid product
Freeze drying
Powdered product
Figure 13.1
Overview of the production of antisera for therapeutic use to induce passive immunization.
Refer to text for specifi c details
Although hypersensitivity reactions can occur upon administration of immunoglobulin prepa-
rations, the incidence of such events is far less frequent than is the case upon administration of
antibody preparations of animal origin. As with all blood-derived products, the serum from which
the immunoglobulins are due to be purifi ed is fi rst assayed for the presence of infectious agents
before its use.
The major polyclonal antibody preparations used therapeutically are listed in Table 13.1. These
may generally be categorized into one of several groups upon the basis of their target specifi cities.
These groups include antibodies raised against:
•
specifi c microbial or viral pathogens;
•
microbial toxins;
•
snake/spider venoms (anti-venins).




Search WWH ::

Custom Search