Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Box 11.4
Female follicular structure
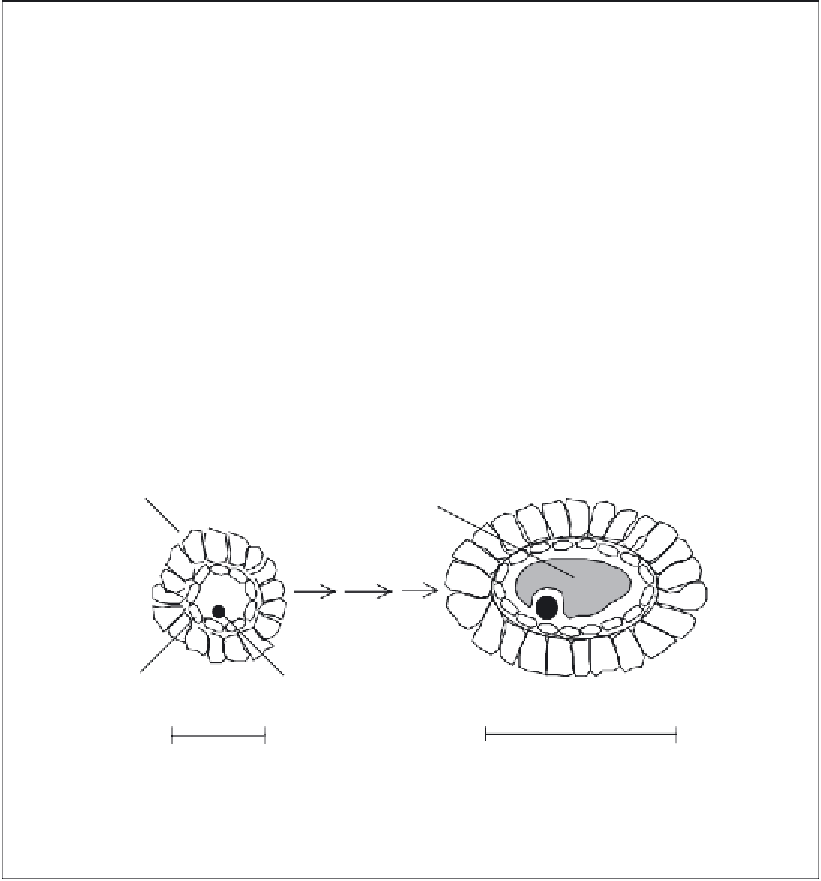
The major female reproductive organs are a pair of ovaries, situated in the lower abdomen. At
birth, each ovary houses approximately 1 million immature follicles. Each follicle is composed
of an egg cell (ovum) surrounded by two layers of cells: an inner layer of granulosa cells and
an outer layer of theca cells. During the follicular phase of the female reproductive cycle (Box
11.3), a group of follicles (∼20), approximately 5 mm in diameter, are recruited by FSH (i.e.
they begin to grow). FSH targets the granulosa cells, prompting them to synthesize oestrogen.
The dominant follicle continues to grow to a diameter of 20-25 mm (Figure 11.B2). At this
stage, it contains a fl uid-fi lled cavity with the ovum attached to one side. Ovulation is charac-
terized by bursting of the follicle and release of the ovum.
Typically, 400 follicles will mature and fully ovulate during an average woman's reproduc-
tive lifetime. The remaining 99.98 per cent of her follicles begin to develop, but regress due to
inadequate FSH stimulation. The molecular detail of how FSH (and LH) promotes follicular
growth is described in the main body of the text.
Theca cells
Fluid filled sac
FSH
Ovum
Granulosa cell
5 mm
~ 25 mm
Mature follicle prior
to ovulation
Immature follicle
Figure 11.B2
Follicular growth
Prior to puberty, serum FSH levels are insuffi cient to promote follicular recruitment and
development. Subsequent to puberty, as a group of follicles begin to develop at the beginning of a
cycle, the one that is most responsive to FSH (i.e. displays the lowest FSH threshold) becomes the
fi rst to secrete oestrogen. As one effect of oestrogen is to suppress FSH release from the pituitary,
blood FSH levels then plateau or decline slightly. This slightly lower FSH concentration is insuf-
fi cient to sustain growth of follicles of higher FSH thresholds, so they die, leaving only the single
oestrogen-producing dominant follicle (Boxes 11.3 and 11.4) to mature and ovulate.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search