Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
1. Apply protein-containing sample
2. Irrigate with buffer (wash out unbound material)
3. Apply elution buffer and collect fractions
Assay for
target protein
A
280
Collect fractions
when elution buffer
is applied
(a)
5
10
15
20
25
30
Fraction number
(b)
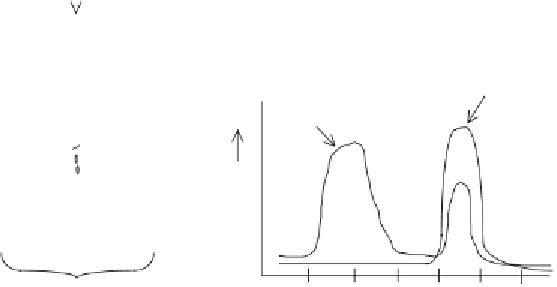
Figure 6.7
(a) Typical sequence of events undertaken during an (adsorption-based) protein purifi cation
chromatographic step. Note that the chromatographic beads are not drawn to scale, and in reality these
display diameters
0.1 mm. Fractions collected during protein desorption are assayed for (i) total protein,
usually by measuring absorbance at 280 nm, and (ii) target protein activity. (b) In the case illustrated, two
major protein peaks are evident, only one of which contains the protein of interest. Thus, desorption and
adsorption steps can result in selective purifi cation
processing columns are available that are manufactured from stainless steel. Process-scale chroma-
tographic separation is generally undertaken under low pressure, but production-scale high-pressure
systems (i.e. process-scale HPLC) are sometimes used, as long as the protein product is not adversely
affected by the high pressure experienced. An HPLC-based 'polishing step' is sometimes employed,
e.g. during the production of highly purifi ed insulin preparations (Chapter 11). Next, we will consider
individually the most common forms of chromatography used to purify therapeutic proteins.
Table 6.2
Chromatographic techniques most commonly used in protein purifi cation protocols. The basis of
separation is listed in each case
Te ch n ique
Ba sis of sepa r at ion
Ion-exchange chromatography
Differences in protein surface charge at a given pH
Gel-fi ltration chromatography
Differences in mass/shape of different proteins
Affi nity chromatography
Based upon biospecifi c interaction between a protein and an
appropriate ligand
Hydrophobic interaction chromatography
Differences in surface hydrophobicity of proteins
Chromatofocusing
Separates proteins on the basis of their isolectric points
Hydroxyapatite chromatography
Complex interactions between proteins and the calcium
phosphate-based media; not fully understood























Search WWH ::

Custom Search