Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
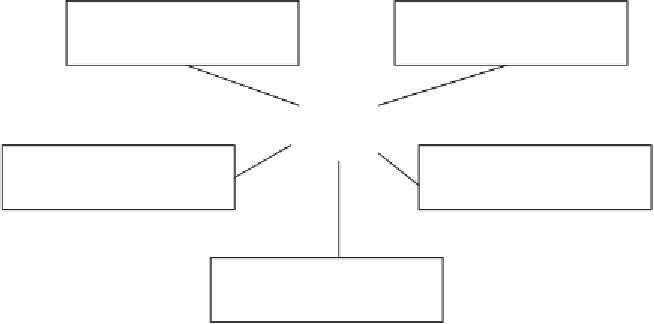
Center for drug evaluation
& research (CDER)
Center for biologics evaluation
& researh (CBER)
FDA
Center for devices
& radiological
health (CDRH)
Center for veterinary
medicine (CVM)
Center for food safety &
applied nutrition
Figure 4.10
Partial organizational structure of the FDA, displaying the various centres primarily responsible
for regulating drugs, devices and food
The major FDA responsibilities with regard to drugs include:
•
assessing preclinical data to decide whether a potential drug is safe enough to allow commence-
ment of clinical trials;
•
protecting the interests and rights of patients participating in clinical trials;
•
assessing preclinical and clinical trial data generated by a drug and deciding whether that drug
should be made available for general medical use (i.e. if it should be granted a marketing licence);
•
overseeing the manufacture of safe effective drugs (inspecting and approving drug manufac-
turing facilities on the basis of compliance to the principles of good manufacturing practice as
applied to pharmaceuticals);
•
ensuring the safety of the US blood supply.
In relation to the drug development process, the CDER has traditionally overseen and regulated
the development and marketing approval of mainly chemical-based drugs. The CBER is more
concerned with biologics. 'Biologic' has traditionally been defi ned in a narrow sense and has
been taken to refer to vaccines and viruses, to blood and blood products, and to antiserum, toxins
and antitoxins used for therapeutic purposes. Because of this, many established pharmaceutical
products (e.g. microbial metabolites and hormones) have come under appraisal by the CDER, even
though one might initially assume they would come under the biologics umbrella. The CDER has
now also been assigned regulatory responsibility for the majority of products of pharmaceutical
biotechnology (Table 4.8).
The criteria used by the CBER and CDER regulators in assessing product performance dur-
ing the drug development process are similar, i.e. safety, quality and effi cacy. However, the
administrative details can vary in both name and content. Upon concluding preclinical trials, all
Search WWH ::

Custom Search