Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Angiotensinogen
Apelin
Vaspin
Hepcidin
NGF
VEGF
HGF
IGF-1
Prostaglandin {PGE2]
Androgen
Estrogen
Adiponectin
Leptin
Visfatin
Vaspin
Omentin
Resistin
MCP1
TNF-a
IL6
IL1
IL1-RA
IL10
CRP
CCL2
CXCL8
CXCL10
CCL5
LPL
FFA
Retinol
Cholesterol
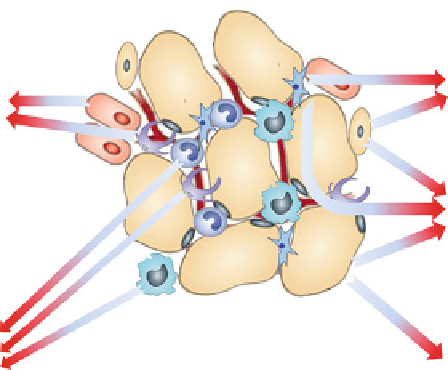
Fig. 2 Bioactive factors secreted by adipose tissue cells. Adipocytes pre-adipocytes, adipose
progenitor cells, macrophages monocytes, and pericytes produce various adipokines comprising
cytokines, angiogenesis, survival, growth and immunomodulatory factors. In addition, adipocytes
secret lipids and other metabolites, as well as steroid hormones
factor regulating energy homeostasis and metabolism in peripheral tissues [
58
].
Its levels are inversely correlated with increased adiposity and cancer progression
[
53
,
59
]. Adiponectin-directed intracellular signaling, mainly through AMP-
activated protein kinase, is critical for modulating insulin sensitivity, vessel
function, and immunity [
51
]. Despite increased circulation of leptin and decreased
circulation of adiponectin observed in obese cancer patients, the exact functions of
these proteins in the tumor are not clearly established. A number of studies suggest
that adiponectin can also act as anti-inflammatory and antithermogenic agent.
Adiponectin has also been shown to suppress neovascularization, suggesting
angiogenesis as a process less restricted upon its downregulation in the obesity/
cancer setting [
60
,
61
].
Some adipokines are mainly secreted by cells of the SVF rather than by
adipocytes in WAT [
62
]. WAT-infiltrating monocytes/macrophages, polarization
of which depends on the pathological obesity state, are the source of many
cytokines. IL-6 is a major candidate link between obesity and cancer [
63
]. The
biological activity of IL-6 is due to its signaling through a cell-surface type I
cytokine receptor complex consisting of the ligand-binding IL-6Ra chain, and the
signal-transducing component gp130. Dimerization of IL-6/IL-6R/gp130 leads to
the initiation of intracellular signaling primarily through the Janus Kinase-Signal














Search WWH ::

Custom Search