Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
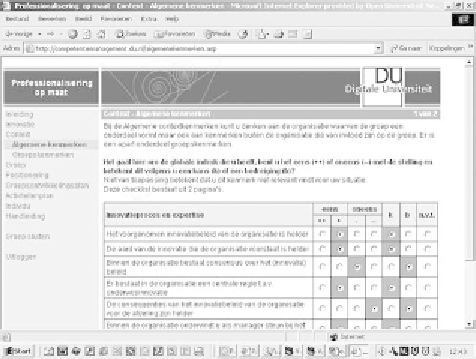
Figure 1. Screenshot of a webtool to identify competences (from Stalmeier, 2006, p. 43)
der Klink and Boon point at the confusion sur-
rounding the concept of competence, which is
clearly illustrated in Table 2.
As this table shows notions on competences
differ strongly which harm the exchangeability
of competence profiles. For example, profiles
applied in companies for performance assessments
cannot be easily transferred into profiles for edu-
cational purposes. It goes without saying that the
further attuning of the various competence profiles
is not going to happen easily but at the same time
this is a prerequisite for the ultimate success of
APL. Especially for this reason, it is important to
define competence profiles in such a way that
others understand the meaning of the profiles.
Different people may interpret the same compe-
tence of the same person at the same time differ-
ently. The question is, which interpretation is
Table 2. Various perspectives on the concept of competences
Perspective
Position
Difference in definition
Geographic
USA
Competency
refers to behaviour and personal traits that contribute to excel-
lent performance
UK
Competence
refers to collectively agreed occupational standards such as
national vocational qualifications
Germany
Kompetenz
refers to the capacity of a person to act. It is more holistic than
competency
or
competence
, comprising not only content or subject matter
expertise but also more generic abilities
Field of application
Training and education
Competences are defined as clusters of skills, attitudes and knowledge that
can be learned
Selection and recruitment
Competences are perceived as partly trainable and as partly rather stable
traits that are difficult to change.
Performance assessment
Competences are mainly defined as the output of tasks and jobs
Underlying learning theory
Cognitivism
Emphasis on observable and measurable performance. Stronger focus on
top-down development of competence-based systems
Constructivism
Stresses values and beliefs as important components of competences.
Stronger focus on employees' participation in the development of
competence-based systems








































Search WWH ::

Custom Search