Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
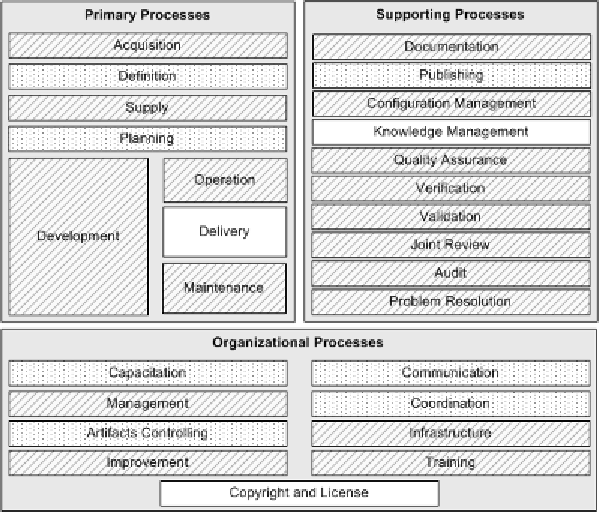
Figure 2. Overall structure of SP-DEM
definition of learning problem and needs for in-
struction
; (2)
initial definition of learning require-
ments
; (3)
analysis of project viability
; (4)
deter-
mination of the module scope
; (5)
construction
of a terminology repository
; (6)
documentation
of the definition process
; and (7)
revision and
approval
. For instance, activity (1) is based on
the analysis stage of the ADDIE model; it involves
the following tasks:
determination of actual learn-
ing conditions
;
definition of learning goals and
related skills
;
prioritization of learning goals
; and
identification of learning discrepancies
.
Activity (5) is especially important since it
involves the construction of a terminology reposi-
tory, i.e. a dictionary of terms about the subject
knowledge domain. This mechanism is relevant
for supporting distributed development teams to
share concepts and related information, and to
adopt a uniform and consistent terminology dur-
ing the entire project. Moreover, the construction
of a dictionary of terms is important not only for
collaboration and distribution perspectives, but
also for the development of “open products”.
Such dictionaries can be extended to knowledge
bases or even domain ontologies (Uschold &
Grüninger, 1996), allowing knowledge sharing
among developers.
The purpose of the
Planning Process
is to re-
view the module's requirements aiming at defining
its structure and establishing the plans to be used for
managing the project and guaranteeing the quality
Table 1. Correspondence among ADDIE model
stages and SP-DEM primary processes
ADDIE Model Stages
SP-DEM Primary Processes
Needs for Instruction
Definition
Front-end Analysis
Development
Planning
Development
Design
Development
Development
Operation
Delivery
Implementation
Evaluation
Maintenance



































Search WWH ::

Custom Search