Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
After setting up the LISL script (either by
scripting or by using the graphical user interface
to compile it with a few clicks), the knowledge
worker can start working with her personal learn-
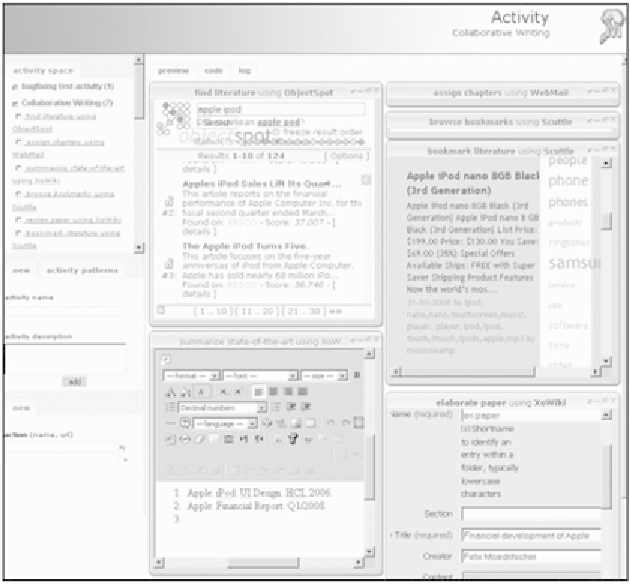
ing environment. For the 'Collaborative Paper
Writing' activity the LISL interpreter creates the
web application mash-up shown in Figure 8. With
this MUPPLE page the knowledge worker can
arrange the tools according to her preferences,
minimize the ones that are not relevant at the time,
and maximize those that require more space or
are of central importance for completing an action.
If the knowledge worker considers one action to
be finished, she can declare this state by simply
clicking on the checkbox next to the action in the
section 'activity space'. If all of the actions are
declared finished the whole activity is marked as
completed.
So far, the scenario primarily showed how one
learner can design her personal learning environ-
ment for a certain activity and work with it. In
order to collaborate with others, the learner has
two possibilities (see Figure 9): on the one hand,
she can simply invite other users to participate in
this activity by using a single learning tool, e.g.,
the Wiki. Thus, the collaborators would be in-
volved into the paper writing activity by editing
the Wiki pages (paper, review) with a standalone
application, but they could not use the other fea-
tures of the activity.
Alternatively, other users might also want to
create a mash-up personal learning environment
for elaborating the paper collaboratively and in-
terface their environments with each other. There-
fore, they can build up their own activity and
receive the most important information. As this
typically involves a lot of articulation work to
Figure 8. MUPPLE page for activity 'Collaborative Paper Writing'
Search WWH ::

Custom Search