Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
14.12.3
Surface waters
14.12.3.1
Sulphide, sulphite and thiosulphate
Various workers [70-72] have discussed the determination of multiple sulphur anions
(sulphide, sulphite and thiosulphate) in non saline waters.
14.12.4
Potable waters
14.12.4.1
Sulphide and cyanide
Jovanovic and Jovanovic [59] determined low levels of sulphide and cyanide using a
deposited on wire silver-silver sulphide electrode.
14.12.5
Waste waters
14.12.5.1
Thiocyanate, cyanate and cyanide
Thieleman [73] attempted the separation of thiocyanate, cyanate and cyanide ions by thin
layer and paper chromatography. Thin layer chromatography was not successful but these
three ions were successfully separated by paper chromatography with the solvent
methanol-pyridine-dioxan (7:2:1) in 7-8 h. Cyanide and cyanate were identified by
means of bromocresol purple and thiocyanate by 15% ferric chloride solution, as spray
reagent. Carbonate ions have the same RF value as cyanide and cyanate.
Cyanide and cyanate in waste water have also been separated by paper
chromatography [74]. Separation is achieved by use of isopropyl alcohol-ethanol-water
(9:4:3) as solvent with Filtrak FN 8 paper. After drying, the paper is sprayed with
bromocresol green solution. On a green background the ions appear as clear blue spots
(R
F
values: cyanide, 0.04, cyanate 0.29). The spots may also be located by treating the
paper with silver nitrate solution and exposing it to hydrogen sulphide.
Thiocyanate has been determined in waste water using a cyanide selective electrode
[75]. In this method thiocyanate is first converted to cyanogen bromide using bromine
water. Excess bromine is removed by the addition of phenol. The cyanogen bromide is
then converted to cyanide by the addition of sulphurous acid and then sodium hydroxide
added. Cyanide was then estimated using the cyanide-selective electrode.

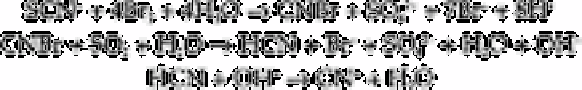
Search WWH ::

Custom Search