Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
As much as 10
5
-10
6
faster
Enzymes
As much as 10
4
-10.
5
faster
Colloidal gels
Complexing cations
Very many-fold faster in most cases
Concentration
Roughly proportional
Ionic environment in the solution
Several-fold change
Source: Reproduced with permission from Elsevier Science [88]
and magnesium determined by atomic absorption spectrometry. The endpoint is indicated
by a sharp rise in the magnesium absorption; features of the titration curve after the end-
point are related to species formed in the flame. Some observations on polyphosphate
titrations are presented, and the method was applied to the determination of phosphate in
surface and waste waters.
Condensed phosphate is a generic title for all phosphates which are formed by the
removal of one or more water molecules from orthophosphoric acid, which may be
represented as 3H
2
O.P
2
O
5
. These include metaphosphoric acid (H
2
O.P
2
O
5
),
pyrophosphoric acid (2H
2
O.P
2
O
5
), ultraphosphoric acid (general formula mH
2
O.P
2
O
5
)
where 0
≤
m<1), and polyphosphoric acid (general formula mH
3
PO
4
-(m—1)H
2
O where
1
≤
m<
∞
). The most common condensed phosphates are pyro- and tripolyphosphate
which have dissociable protons and behave as typical polyprotic acids. The
pyrophosphate and tripolyphosphate each occur in three forms
pyrophosphates
tripolyphosphates
A number of factors affect the rate at which condensed and organic phosphates undergo
hydrolytic degradation in aqueous solution. The major environmental factors in
decreasing order of effectiveness are listed in Table 8.20. Consideration of Table 8.20
indicates that pH is one of the factors which exerts a considerable influence on the rate of
hydrolysis.
In a domestic waste water, all these factors may influence the hydrolysis of condensed
phosphate to orthophosphate. Thus if the sample is not analysed immediately, changes in
the concentrations of condensed and orthophosphates will occur. If the forms of
phosphate are to be determined rather than total phosphate, hydrolysis must be prevented.
8.17.4
Ion chromatography
The application of this technique is discussed under multianion analysis in sections 12.7.1
and 12.7.2.
8.17.5
Ion exclusion chromatography
The application of this technique is discussed under multianion analysis in section

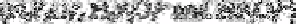
Search WWH ::

Custom Search