Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
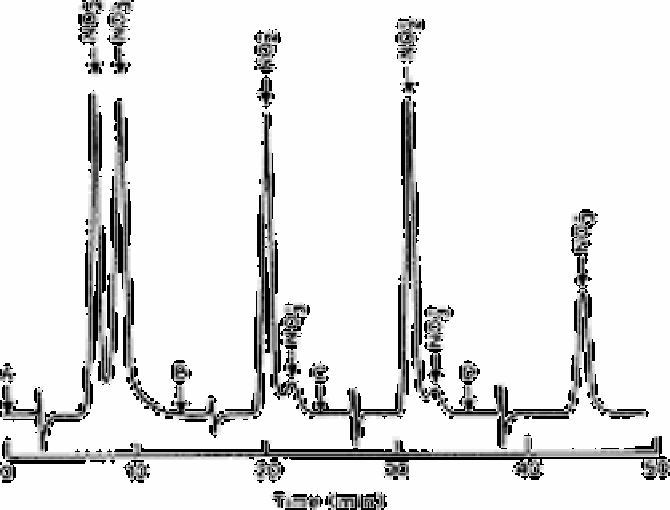
Fig. 7.11
Chromatograms resulting from the injection of samples containing
nitrate and nitrite into a mixed bed column containing Kieselguhr and
Ecteola ET 41 cellulose anion exchanger
Eluant:0.03M K
2
SO
4
, 0.01M Tris buffer (pH 7); A. Standard mixture
containing 1.4mg L
−1
as nitrogen of both nitrite and nitrate
(attenuated 0.1); B, sewage sludge sample, diluted 1:100 containing
2.7mg L
−1
as nitrogen of nitrite and 0.35mg L
−1
as nitrogen of nitrate
(attenuation 0.2); C, sewage sludge sample, diluted 1:100 containing
1.4mg L
−1
as nitrogen of nitrite and 0.1 ml L
−1
as nitrogen of nitrite
(attenutate 0.11); D, potable water containing 0.45mg L
−1
as nitrogen
of nitrate (attenuation 0.1)
Source: Reproduced with permission from Elsevier Science [71]
A stainless steel column (SS 316) of length 30cm and i.d. 0.3cm was filled with a mixture
of Kieselguhr and Ecteola ET 41 cellulose anion exchanger (Whatman: W & R Balston,
Maidstone, UK). The eluent used was 0.03M potassium sulphate solution and 0.01M Tris
buffer at pH 7 in water.
A ratio of Kieseiguhr to Ecteola of 1:2 (by weight) was used. The column was operated
at a pressure of 40 bar. The eluant was monitored with a Cecil CE-212
spectrophotometric flow through detector at a wavelength of 210nm. The temperature of
the column was ambient. Samples were injected with the aid of a sample injection valve
(Valvo C20) using a sample loop of 60µL.
Examples of chromatograms of potable water and of sludge solution resulting from
Search WWH ::

Custom Search