Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
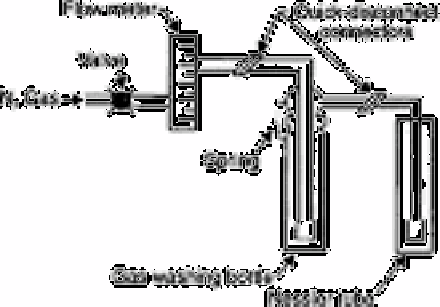
Fig. 2.53
Gas train apparatus for evolution and adsorption of sulphite
Source: Reproduced with permission from Elsevier Science [843]
allowing the octyl alcohol to rise to the surface. The concentration of sulphite ion was
calculated from a calibration curve obtained by analysing a procedure blank and several
stabilised sulphite standards.
Good agreement was obtained between results obtained by this procedure and those
obtained by the standard iodometric procedure [844].
2.95.2
Spectrophotometric methods
Sulphite has been determined in water [843] by a process involving acidifying the sample
and purging with nitrogen to strip out sulphur dioxide, which is then absorbed in a
solution containing ferric iron and 1,10-phenanthroline; the ferric iron is reduced to the
ferrous state by the sulphur dioxide, and an orange tris-(1,10-phenanthroline)iron
complex is formed, which can be quantified spectrophotometrically at 510nm after
removal of excess ferric iron with ammonium bifluoride. The effects of temperature and
the removal of interferences are described. The detection limit is 0.01mg L
−1
sulphite.
Good agreement was obtained between results produced by this procedure and those
by the standard iodometric procedure [844].
Williams [845] and West and Gaebe [846] determined sulphite spectrophotometrically
by the
p
-rosaniline method. Sulphate reacts with mercuric chloride to form a
dichlorosulphurmercurate complex. After the addition of formaldehyde and
p
-rosaniline
the coloured
p
-rosaniline-methyl sulphonic acid is formed and this is evaluated
spectrophotometrically at 560nm.
Sulphite, sulphate and dithionate have been determined spectrophotometrically in the
presence of each other [293].
The sulphur(IV) catalysis of the oxidation of cobalt(II) by dissolved oxygen forms the
basis of a spectrophotometric method for determining sulphite in aqueous solutions in
non saline waters [847]. The cobalt(III) produced is reacted with azide to form a complex
having a strong absorption at 365nm. A working range of 5×10
−7
to 5×10
−5
mol of
Search WWH ::

Custom Search