Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
Palladium complexes
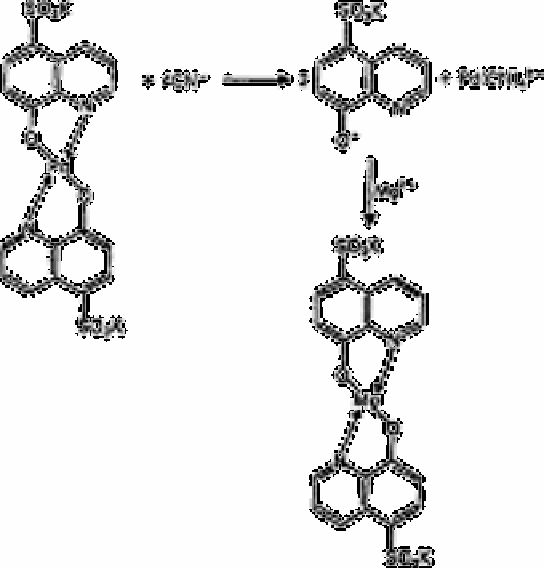
A rapid and sensitive method has been developed for the determination of microgram
amounts of sulphide and cyanide [253]. This method depends on the demasking of
quinolin-8-ol-5-sulphonic acid by cyanide or sulphide from the non-fluorescent
potassium bis(5-sulphoxino)-palladium. The liberated quinolin-8-ol-5sulphonic acid then
coordinates with the magnesium ion present to form a fluorescent chelate, which is a
measure of the amount of cyanide or sulphide present. The reactions are shown below.
Cyanide can be determined by a method [254] based on the liberation of piazselenol
naphtho(2,3-c)(1,2,5)selenadiazole (L) from the Pd
2
L
2
Cl
4
complex [255]. The organic
reagent is then extracted into hexane and its fluorescence is measured.
Pyridoxal and pyridoxal-5-phosphate complexes
Bonavita [256] studied the reaction of pyridoxal and pyridoxal-5-phosphate with cyanide.
This anion produces a catalysed oxidation of pyridoxal to the lactone of 4-pyridoxic acid
[257]. The rate of the reaction is measured by measuring the fluorescence intensity. The
method consists in treating cyanide with pyridoxal at pH 7.5 and measuring the
fluorescence intensity at pH 10.
Chloramine and nicotinic acid
A method has been proposed for the determination of cyanide based on its reducing
reaction with chloramine-T and nicotinamide [258]. Cyanide is converted into cyanogen
Search WWH ::

Custom Search