Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
greater.
Most of these methods for the determination of borate are highly sensitive. The method
using dibenzoylmethane [50,51] (0.5ng ml
−1
), quercetin [52,53] (0.3ng ml
−1
) or 2-
hydroxy-4-methoxy-4
′
-chlorobenzophenone [54] (0.4ng ml
−1
) are the most sensitive.
These methods are based on the formation of an ion association ternary or binary
anionic complex associated with a basic dye cation that generally belongs to the family of
the rhodamines, (see formula p.108).
Haddad [55] published an extensive review on the application of ternary complexes to
spectrofluorometric analysis.
Several rhodamines (Rhodamine S, Rhodamine 6G and Butylrhodamine B) were
compared as reagents for the determination of boron [56] by measurement of the
luminescence of their compounds with BF
4
in benzene solution. Butylrhodamine B was
the best reagent The addition
Name
Substituent
Rhodamine B
Butyrihodamine B
Rhodamine 6G
R
1
C
2
H
5
C
2
H
5
H
R
2
C
2
H
5
C
2
H
5
C
2
H
5
R
3
C
2
H
5
C
2
H
5
H
R
4
C
2
H
5
C
2
H
5
C
2
H
5
R
5
CH
3
H
H
R
6
H
H
CH
3
R
7
C
4
H
9
C
2
H
5
H
of acetone to the benzene extract increased the luminescence considerably in
determinations with Butylrhodamine B, and the addition of acetone to the aqeous phase
before the extraction with benzene increased the intensity of luminescence of the extract
in determinations with Rhodamine 6G. In a further paper Babko
et al.
[57] used the same
method with Butylrhodamine B but having previously removed the cations with an ion
exchange resin in the acidic form.
Boron has been determined with salicylic acid and Rhodamine 6G [58, 59]. The excess
of salicylic acid was removed, after evaporating the solution to dryness, by complexing it
with iron(III). The complex of boron was extracted into benzene. The data were used for
the development of a luminescence method for the determination of boron in waters [60].
In methods based on formation of complexes, the anion reacts with either one or two

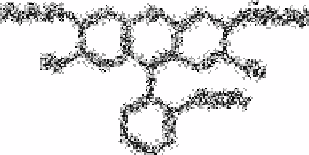
Search WWH ::

Custom Search