Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
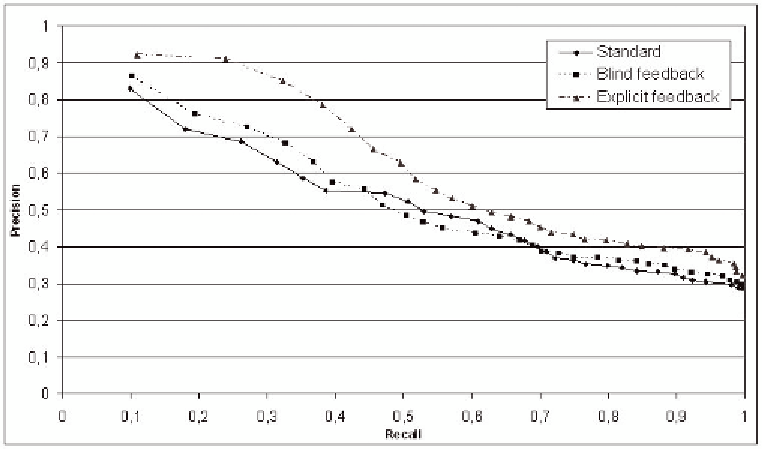
Figure 5. Experimental results
In our approach we use the last strategy to perform our experiments. The document collection is
split randomly in order to consider documents from all topics. The random function is calculated on
each single category. The used test set simulates a “real” search on the Web because we analyze the
pages that are fetched from a standard search engine and we consider also problems such as “page not
found,” “redirecting” and so on.
In Figure 5 the trend of the experimental results is shown: For low recall values, the precision is high
with all strategies. This is a suitable effect in IR retrieval systems because the real relevant documents
are immediately presented to the user moreover RF techniques improve the results accuracy with re-
spect our standard strategy (without RF) because by increasing the recall the precision also improves.
We note that the blind RF strategy gives an initial improvement but it is lower than the standard one
because the system considers false positives in the feedback step.
conclusion
We have described a system and a novel metric to improve ranking accuracy in IR on the Web, using
relevance feedback techniques, discussing a hybrid approach that takes into account both syntactic,
Semantic and statistical information; we also described a general knowledge base used to dynamically
extract a Semantic network for representing user information needs.
Many other topics could be further investigated such as: (1) Using implicit feedback and user char-
acteristics; (2) adding relevance terms to user query refinement to consider new documents after the
first interaction; (3) considering multimedia information to perform RF on other features different to
textual ones; (4) inferring relevant documents and related terms in order to have specialized ontologies
merged with the proposed DSN.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search