Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
The dynamic Semantic network
In the proposed system, the implementation of the ontology is obtained by means of a Semantic network
(i.e., DSN), dynamically built using a dictionary based on WordNet. WordNet organizes several terms
using their linguistic proprieties. Moreover, every domain keyword may have various meanings (senses)
due to the polysemy property, so a user can choose its proper sense of interest. In WordNet these senses
are organized in synsets composed of synonyms; therefore, once the sense is chosen (i.e., the appropriate
synset), it is possible to take into account all the possible terms (synonyms) that are in the synset. Beyond
the synonymy, we consider other linguistic properties applied to typology of the considered terms in
order to have a strongly connected network. The DSN is built starting from the domain keyword that
represents the context of interest for the user. We then consider all the component synsets and construct
a hierarchy based on the hyponymy property; the last level of our hierarchy corresponds to the last level
of WordNet's hierarchy. After this first step, we enrich our hierarchy by exploiting all the other kinds of
relationships in WordNet. Based on these relations we can add other terms to the hierarchy obtaining
a highly connected Semantic network.
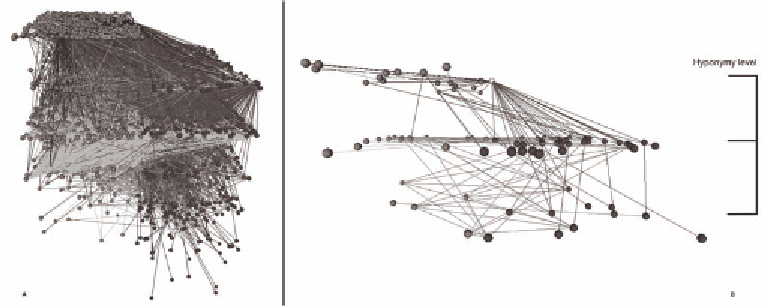
Figure 2 shows an example of DSN. Figure 2 (A) represents the music domain; we can see the high
complexity of the network, due to the generality of the chosen term. On the other hand, Figure 2 (B)
shows a Semantic network about the concept car; in this figure we can see better the network structure
organized around the hyperonymy/hyponymy hierarchy.
The arcs between the nodes of the DSN are assigned a weight σ
i
, in order to express the strength of the
relation. The weights are real numbers in the [0,1] interval and their values are defined experimentally.
To calculate the relevance of a term in a given domain we assign a weight to each element in the DSN
considering the polysemy property (that can be considered as a measure of the ambiguity in the use of
a word, when it can assume several senses). Thus we define the centrality of the term i as:
1
(1)
( )
i
=
poly i
( )
Figure 2. An example of DSN: (A) Music, sense 1; (B) Car, Sense 1

Search WWH ::

Custom Search