Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
FIGURE 17.3
Biosynthesis of LPS. IM and OM are the inner and outer membranes respectively.
O antigen is synthesized separately from lipid A-core through either the Wzy- or ABC transporter-
dependent pathway. Lipid A-core is synthesized on the cytoplasmic face of the inner membrane,
then flipped to the periplasm by MsbA where it can be ligated with the O antigen. The completed
LPS molecule is then exported to the cell surface by the Lpt proteins where it makes up the majority
of the outer membrane.
established by the efforts of Christian Raetz and his research group, leading
to what is often known as the '
Raetz pathway
'. In this conserved pathway,
formation of tetraacyl lipid A (called lipid IV
A
) is followed by addition of the
two inner core Kdo residues before the secondary acyl chains can be added to
complete the hexaacyl lipid A. Once the lipid A-core is complete, it is flipped
to the periplasmic side of the inner membrane by MsbA, an essential protein
belonging to the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter superfamily. MsbA
plays a crucial role in quality control of lipid A structure since it has a prefer-
ence for hexaacyl lipid A over earlier intermediates (such as lipid IV
A
) as a
substrate (
Doerrler and Raetz, 2002
). As a result, the minimal LPS structure for
export and cell viability is normally considered to be Kdo
2
-lipid A. However,
suppressor mutants lacking Kdo (and therefore also devoid of secondary acyl
chains) are viable, albeit with a compromised outer membrane barrier, leading
to LPS molecules comprising lipid IV
A
(
Meredith et al., 2006
). Alternatively,
the absence of Kdo can also be overcome by overexpression of the second-
ary acyltransferases to generate pentaacyl and hexaacyl free lipid A (
Reynolds
and Raetz, 2009
). After export of lipid A-core to the periplasmic face of the
inner membrane, the ligase enzyme (WaaL) covalently links it to the O antigen,
which is synthesized separately.

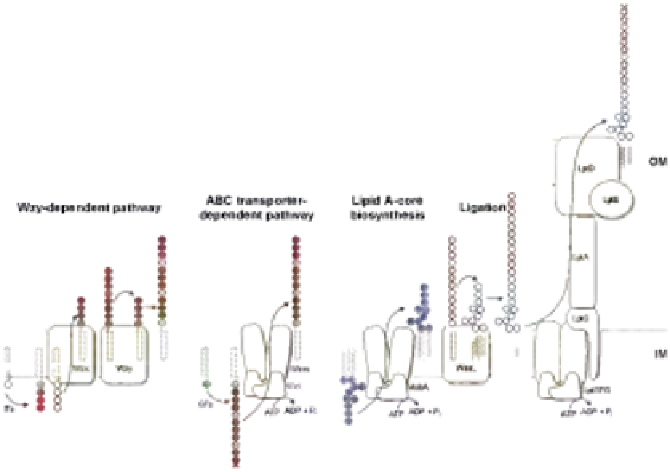
Search WWH ::

Custom Search