Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
adhesive functional tip away from the cell surface (
Klemm et al., 2004; Junker
et al., 2006
).
The β-helical structure of the passenger domain also allows functional groups
to be inserted within turns that protrude from the β helix without disturbing its
structural integrity (
Emsley et al., 1996
). These functional groups can be small,
such as the tripeptide Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) adhesion motif of the
E. coli
adhesin
Antigen 43 (
Fernandez and Weiss, 1994; Klemm et al., 2004
) or large globular
domains with various activities. The serine protease ATs of
Enterobacteriacae
(SPATEs) are the best examples of this globular structure. The crystal structures
of three
E. coli
SPATE proteins, Hbp, EspP, and Tsh, have been solved with all
including an extended right-handed β-helical structure that forms the spine and a
globular subdomain reminiscent of the chymotrypsin family of serine proteases,
which carries the proteolytic function of the passenger. In Hbp and Tsh there is
also a second subdomain (termed domain 2) that adopts a chitinase b-like fold
but for which a functional role has not yet been identified (
Figure 16.5
).
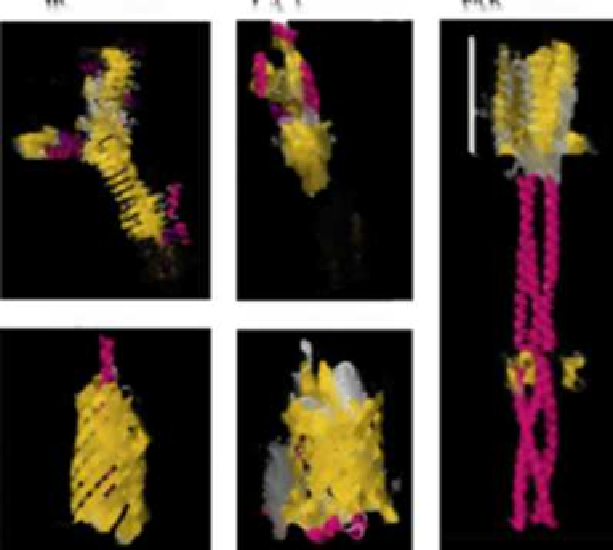
FIGURE 16.5
Crystal structures of the passenger domains of
E. coli
T5SS proteins. Hbp is a type
5a secreted SPATE with the typical stacked β-helices and globular domain. The β-barrel is com-
posed of 12 strands with an α-helix linker. Intimin is a type 5e secreted protein with three Ig-like
domains and a lectin-like domain which binds Tir. The β-barrel is composed of 12 strands with a
periplasmic LysM domain. EibD is a type 5c secreted protein. Trimeric in structure it has clear head,
stalk and neck regions.
Figures adapted from protein databank (
Otto et al., 1998; Luo et al., 2000;
Tajima et al., 2010; Leo et al., 2011; Fairman et al., 2012
).


Search WWH ::

Custom Search