Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
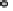
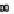
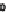
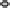
(C)
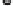
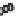
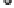
(A)
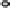
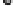
(B)
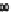
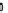
FIGURE 15.4
(A) Within a single microvillus a core of F-actin is stabilized by myosin 1a:calmodulin bridges to the plasma membrane. The F-actin core is teth-
ered into the cellular actin filaments which contain amongst other proteins, myosin 2. EspB can interrupt myosin:actin binding causing microvilli retraction and
effacement. (B) Map and EspF are involved in relocalizing the Na
+
/glucose co-transporter SGLT1 to reduce its function. The Na
+
/H
+
exchanger 2 (NHE2) activity
is decreased by EspF, while EspG and EspG2 induce the internalization and hence reduce the activity of the down-regulated in adenoma (DRA) Cl
-
/OH
-
exchanger.
EspG and EspF, either directly or indirectly, contribute to the mis-localization of aquaporins (AQP). These changes result in increased Na
+
, Cl
-
ions, and water in
the lumen during infection manifesting as watery diarrhea. (C) Tight junction proteins regulate the passage of ions and electrolytes across the gut epithelium. Map
and EspF redistribute the tight junction protein occludin, while EspI/NleA disrupts protein trafficking and hence replenishment of the tight junction proteins which
are highly dynamic requiring constant renewal.





























































































































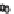





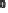


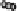























































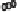































































































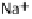
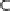









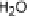





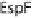


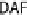

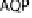






























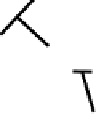
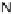


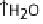
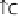


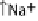
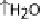



























































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search