Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
(E)
(F)
FIGURE 15.3
T3SS effectors from EPEC (Cif) and
Shigella
(IpaB) interfere with the host cell cycle.
(A) At the cell cycle checkpoint between G2 and M phases, p21 is sent for degradation by neddylated SCF
allowing the activation of Cdk1-cyclin B complex. (B) T3SS effector Cif methylates NEDD8 and inhib-
its SCF, blocking the formation of the Cdk1-cyclin B complex and inducing cell cycle arrest in G2/M
phases. (C) At the cell cycle checkpoint between G1 and S phases, p21 and p27 are sent for degradation
by the neddylated SCF allowing the activation of Cdk2-cyclin A/E complex. (D) The T3SS effector Cif
methylates NEDD8 and inhibits SCF blocking the formation of the Cdk2-cyclin A/E complex and induc-
ing cell cycle arrest in G1/S phases. (E) During the early phase of mitosis the inhibitor of Cdc20, Emi, is
phophorylated by Plk1 releasing Cdc20 and activating the complex APC/Ccdc20. During anaphase, Cdh1
is released from its inhibitor MAD2B to activate the complex APC/Ccdh1 sending Cdc20, Plk1, and
cyclin B for degradation. (F) The T3SS effector IpaB from
Shigella
activates during the G2 phase Cdh1,
by binding its inhibitor MAD2B inducing the unscheduled destruction of Cdc20, Plk1, and cyclin B and
blocking cells in G2/M phases.
Manipulating host cell death
Cell death participates in the renewal of the epithelium, cell maturation and
response to infections. Controlled cell death (apoptosis) allows the organism
to eliminate damaged or infected cells with few consequences for the organs,







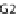






























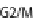













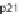






































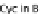






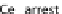
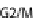



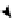

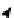










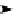

















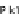






















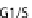


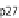






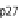


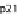






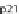





































Search WWH ::

Custom Search