Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
(B)
(A)
(C)
FIGURE 15.2
T3SS effectors from EPEC, EHEC, and
Shigella
interfere with host inflammatory pathways. (A) Infection of EPEC and EHEC results in the stimu-
lation of TLRs and subsequent activation of inflammatory pathways. NleE, NleB, NleH, NleC and NleD T3SS effectors systematically dampen NF-kB and MAPK
activation by targeting key regulatory proteins such as TAB2/3, IκBα, JNK, p38, and p65. (B)
Shigella
activates inflammatory pathways by stimulation of both NLRs
and TLRs. OspZ, OspG, OspI, IpaH9.8, and OspF are involved in the subversion of NF-kB and MAPK pathways by targeting for example UBC13 UbcH5, NEMO/
ABIN-1, and histone H3. (C)
Shigella
escape autophagy by secreting IscB T3SS effector: Depending on the availability of IcsA, which is recognized by both IscB or
Atg5,
Shigella
can be either trapped in septin cages or spread cell-to-cell via actin-based motility.





























































































































































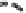











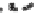











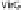






















































Search WWH ::

Custom Search