Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
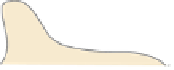
FIGURE 15.1
T3SS effectors from EPEC, EHEC, and
Shigella
interfere with host cytoskeleton. (A) EPEC and EHEC intimately attach and create pedestals on host
cells. The bacterial outer-membrane protein, intimin, interacts with the T3SS effector Tir in the host cell membrane. In some EPEC strains Tir is phosphorylated at
Y474 promoting interaction with the host adaptor protein Nck and recruitment of neural Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (N-WASP). EHEC Tir lacks Y474 instead
utilizing a NPY458 motif to promote actin polymerization. Tir NPY458 interacts with IRTKS/IRSp53, which binds another T3SS effector TccP/EspFU which in turn
recruits N-WASP. In both cases N-WASP recruits the ARP2/3 complex to initiate actin polymerization. N-WASP independent activation of Arp2/3 by TccP/EspFU
has also been described and EspH can recruit N-WASP and N-WASP interacting protein (WIP) to the pedestal independent of Tir residues Y474 and NPY458. In addi-
tion Tir can interact with phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) and the inositol-5-phosphatase SHIP2 to regulate actin accumulation in the pedestal through membrane
phosphoinositide signaling. EspL2 interacts with Annexin2 (Anx2), increasing aggregation of Tir-induced actin. (B) Nanometer-thin micropodial extensions (NMEs)
can interact with the
Shigella
T3SS effectors IpaB and IpaC and trigger NME retraction bringing the bacteria towards the cell. Invasion occurs through a combination
of T3SS effectors; manipulation of Rho GTPases by IpgB1 and 2 (see Figure 15.1C), actin rearrangement through IpaC recruitment of Src, membrane and cytoskel-
eton dissociation by PIP2 to PIP conversion by IpgD and actin depolymerization by IpaA interaction with vincullin. (C) Rho GTPases cycle between inactive (GDP
bound) and active (GTP bound) forms. Rho GEFs activate Rho GTPases by exchanging GDP for GTP and can also participate in binding effector proteins to influence
downstream signaling pathways. T3SS effectors from EPEC/EHEC (Map, EspM, and EspT) and
Shigella
(IpgB1 and IpgB2) mimic Rho GEFs by binding to, and
inducing a conformational change in, their respective Rho GTPases to allow GTP binding and activation. The T3SS effector Cif blocks RhoA degradation resulting
in stress fiber formation while EspH inactivates one subset of mammalian Rho GEFs.










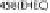


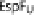
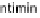






















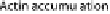





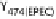





































































































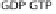



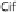












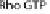

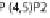



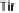

































Search WWH ::

Custom Search