Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
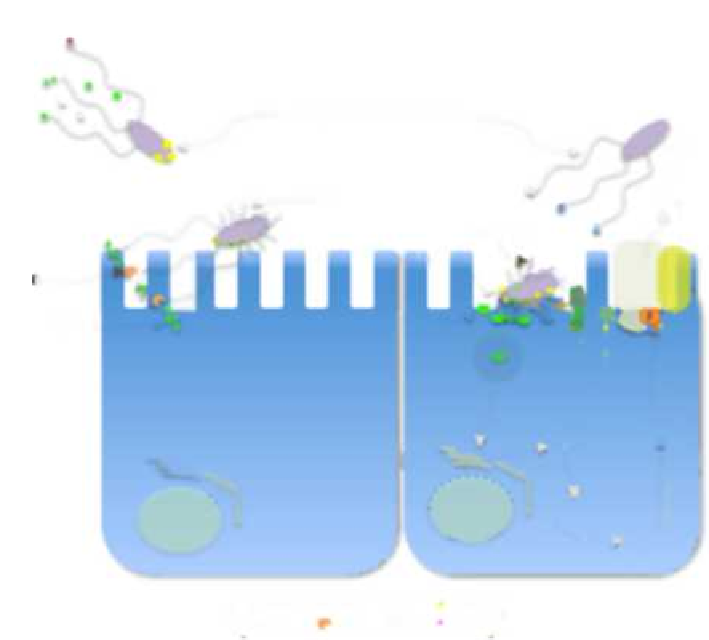
FIGURE 6.4
Summary of steps in molecular pathogenesis of ETEC. Panel on the left shows
motile ETEC expressing the EtpA extracellular adhesin (green circles) which binds to the ends
of flagella in the absence of the flagellar cap structure (FliD, red), and anchors ETEC via its
flagella to the host cell surface. EtpA-mediated binding is modulated by EatA, a secreted auto-
transporter protease. Subsequent steps in ETEC adhesion to intestinal epithelial cells include
binding via fimbrial antigens including colonization factors (CFs), and type 1 fimbriae, as
well as a fimbrial outer membrane proteins including EaeH, which is activated on ETEC-host
cell contact. Efficient delivery of LT and ST requires intimate interaction of bacteria with the
epithelial cells such that LT can bind to GM-1 gangliosides and ST can engage guanylate cyclase
C (GC-C). Binding of LT to the surface triggers toxin internalization and retrograde process-
ing via the trans-Golgi network into the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) (
Wernick et al., 2010
).
The enzymatically active LT A1 subunit is ultimately transported into the cytosol where in the
presence of ADP ribosylating factors (ARFs) it transfers ADP-ribose from NAD to the het-
erotrimeric G protein, GSα,which in turn leads to constitutive activation of adenylate cyclase.
The resulting rapid increases in cAMP activate protein kinase A (PKA) which phosphorylates
CFTR activating the chloride channel. ST peptides (ST-P and ST-H) both engage the extracel-
lular portion of guanylate cyclase C (GC-C) homodimers on the epithelial surface resulting
in signal transduction to intracellular catalytic domain where GTP is converted to cGMP. The
increases in cGMP activate membrane-associated cGMP-dependent protein kinase (cGKII or
PKG) which also phosphorylates CFTR. Intracellular increases in both cyclic nucleotides result
in efflux of cAMP (through MRP channels) and cGMP (through MRP5). ETEC may be pro-
grammed to respond to extracellular increases in cAMP by modulating cAMP-CRP-dependent
gene transcription.

Search WWH ::

Custom Search