Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
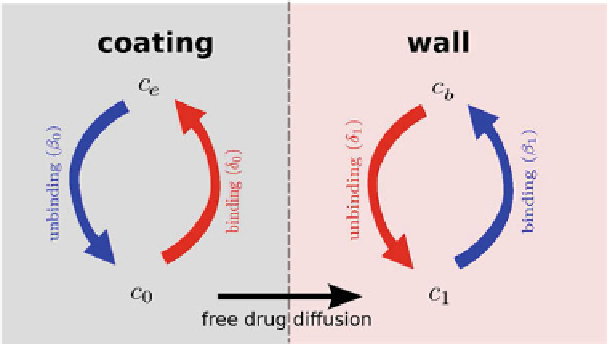
Fig. 2
Schematic of the cascade mechanism of drug delivery in the coating-wall coupled system.
An unbinding (resp. binding) reaction occurs in the coating (resp. in the wall) (
blue arrows
). In both
layers, reverse reactions (
red arrows
) are present in a dynamic equilibrium. Drug transport occurs
only in the free phases
c
0
and
c
1
In this paper we are interested in non-local mass transfer processes in the coating,
where the drug passes from a solid (polymer-encapsulated,
c
e
) to a free phase (
c
0
)
by dissolution. Similarly, a part of the dissolved and transported drug in the wall
(
c
1
) is metabolized by the cells and transformed to a bound state (
c
b
). Thus, the
drug delivery process starts in the coating and ends at the SMC receptors, with bidi-
rectional phase changes in a cascaded sequence, as schematically depicted in Fig.
2
.
Amicroscopic approach would require knowledge of the specific and local geometry
of the individual pore structure networks, which is unfeasible. Therefore, both the
polymeric matrix and the wall are treated as macroscopically homogeneous porous
media with volume-averaged concentrations. Even though we are only considering
the 1D case in this study, we will express concentrations in units of mol m
−
3
. These
chosen units have no influence on the results.
2.1 The Two-Phase Coating Model
The coating of a DES consists of a porous polymeric matrix that encapsulates a
therapeutic drug in solid phase; as such, it is unable to diffuse and to be delivered
into the tissue [
5
]. Nevertheless, when expanded and deployed into the wall, the
stent coating is exposed to the surrounding biological fluids. As a consequence, such
fluids fill the interstitial spaces of the polymer and form a network of liquid channels,
acting as a release medium for the drug. Thus, a fraction of the drug mass is first
transferred, in a finite time, to the liquid phase, and then released and diffuses into
the arterial wall. We carry out a mesoscale description of the volume-averaged drug