Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Here again
m
denotes the total tissue density. Unlike the original model, where each
tissue growth was capped by its individual local density through the term
(
−
m
j
)
,
a competition between the growing tissues was implemented by using the
m
in
this case. Growth factors taking part in bone repair are grouped into osteogenic,
chondrogenic and angiogenic growth factor concentrations. These concentrations,
indicated by index
k
1
=
c
,
b
,v
, are given by diffusion-reaction equations of the form
∂
g
k
∂
=∇
(
D
k
∇
g
k
)
+
R
pr od
,
k
(
g
k
,
m
j
)
c
i
−
R
deg
,
k
g
k
,
(3)
t
where
D
k
is the diffusion coefficient and
R
k
are production and degradation terms.
Growth factor production depends on the biochemical milieu and the respective cell
populations
c
i
.
2.1 Mechanical Stimulation
An isotropic hyperelastic material law is used for the callus region, assuming a
nearly incompressible material for the soft tissues. As a measure for local mechanical
demand
ʵ
V
ʷ
within the callus the equivalent deviatoric strain
is used
1
6
((ʵ
1
−
ʵ
2
)
2
√
3
ʷ
:=
ʵ
V
+
(ʵ
2
−
ʵ
3
)
+
(ʵ
3
−
ʵ
1
)
=
2
2
2
).
(4)
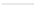
The level of mechanical excitation
ʷ
then defines stimuli parameters
ˈ
l
, with
=
,
,
l
f
denoting osteogenic, chondrogenic and fibrogenic stimulation, as in-
dicated in Fig.
1
. The parameters
b
c
ˈ
take on values between 0 for no and 1 for a
maximal stimulation.
The implementation of the stimulations
ˈ
l
is presented for the stem cell equation,
∂
c
m
∂
=∇[
D
m
∇
c
m
−
C
m
(
∇
g
b
,
∇
g
v
,
∇
m
)
c
m
]+
A
m
c
m
(
1
−
c
m
)
t
−
(ˈ
b
F
1
+
ˈ
c
F
2
+
ˈ
f
F
4
)
c
m
.
(5)
Fig. 1
Definition of stimulation parameter
ˈ
by mechanical excitation levels
ʷ