Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
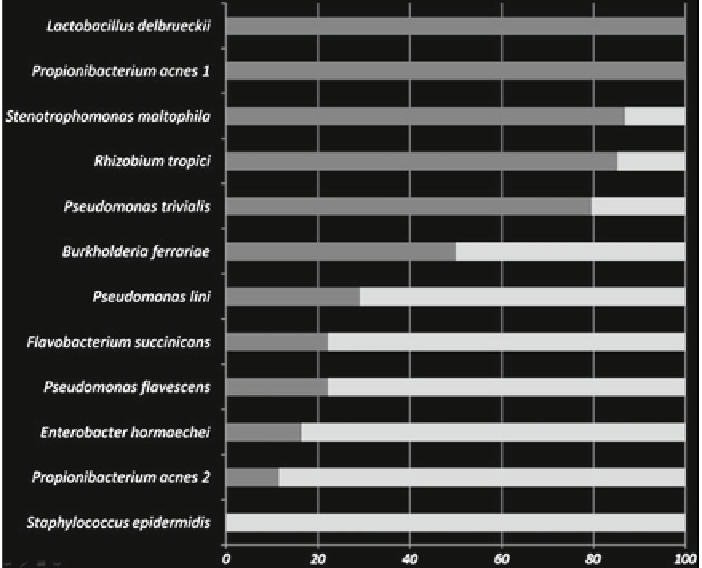
Fig. 2
The distribution of bacteria between asymptomatic (
light grey
) and infected devices (
black
bars
)
while other species were indicators for infectious biofilm communities (Fig.
2
). It is
here interesting to note that two closely related bacterial species have been detected,
here denoted
Propionibacterium acnes
1 and 2. While
P. acnes
1 was mainly found in
asymptomatic biofilm communities,
P. acnes
2 was a member of infectious biofilms.
This observation underlines the importance of virulence factors which may play in
some cases a more important role than the phylogeny of the bacteria.
2.3 Biofilms on Asymptomatic Implants in a Non-sterile
Environment
The current understanding is that pacemakers or bone implants are placed into a
sterile environment. But what happens to implants which are surrounded by bacteria?
The skin, the gut or the mouth are always populated by a large number of bacteria,
nevertheless, the mucosa and/or epithelial cells separate these microorganisms from
the sterile tissues [
19
]. Their function as a barrier is of utmost importance for the entire
organism. Implants for teeth breach this barrier and we became interested in their
biofilms. As for the rhythm management devices we compared biofilm communities
of asymptomatic and infected implants.