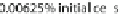Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
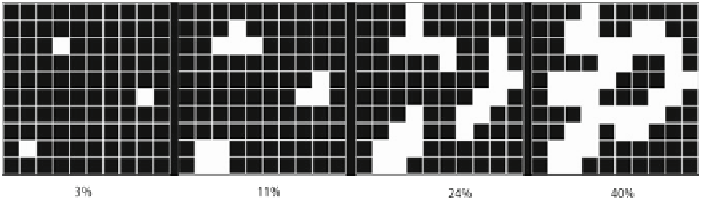
Fig. 1
Illustration of the RVE generating algorithm. Material is agglomerated randomly around
existing material
Fig. 2
Agglomerated material of different structures is emerged from varying number of initial
cells.
Left
0.00625%,
middle
0.2% and
right
6.4% initial cells, all with 25% volume fraction in a
grid of 50
×
50
×
50
A simple algorithmgenerates randomRVE structures in three steps. First an initial
number of cells are randomly assigned with material within a three-dimensional grid.
Afterwards additional cells are randomly selected, but only assigned with material,
if they are adjacent to existing material. This is done until a given volume fraction is
reached. In a final step, all remaining grid cells are assigned with the matrix material.
This algorithm is illustrated in Fig.
1
.
While the volume fraction is directly regulated, the RVE structure develops indi-
rectly by the number of initial cells. A rather rough cluster with highmaterial agglom-
erations emerges from a small number of initial cells, whereas a fine dispersed cluster
emerges from many initial cells. Figure
2
shows three different RVEs, each with 50
elements per edge and equal volume fraction but varying number of initial cells.
2.2 Continuum Mechanics Approach
The continuum mechanics approach is used to calculate three-dimensional mate-
rial deformations. For static considerations the momentum balance of the current