Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
As it is seen from Table 2.2 all compounds, being investigated, possess high thermal
stability. Temperatures of melting and beginning of decomposition are within the range
T
melt
=295-435
0
C and T
dec
=327-395
0
C and this shows potential possibility to introduce
compounds XL-XLIII into PCA melt, as their thermal stability exceeds the temperature of
PCA production and shaping.
Investigations on solidity and stability of XL-XLVI compounds at the stage of ε-
caprolactam polymerization were carried out to determine compatibility and stability of bis -
(1', 8' - benzoilene - 1,2 - benzimidazoles) and bis - (1', 8' - naphthoilene - 1,2 -
benzimidazoles) in reactive PCA mass. Obtained coloured polymer was investigated visually
to homogeneity of solid solution, its solubility in H
2
SO
4
, in the mixture of 80% formic and
trifluoro - acetic acids in ratio 1:1 and in m - cresol. Ability of PCA melt to form into a fibre,
and also molecular masses of dyed and undyed polymer with average viscosity were defined
too.
Polymerization of
ε
- caprolactam in the presence of XL - XLVI compounds was carried
out in ampoules. Thick transparent polymer mass dyed in different colours (from lemon
colour to yellow) depending on applied compound was obtained in all ampoules after 6-
hours' synthesis. When using all the compounds initial colour of the melt did not change.
This shows stability of investigated compounds in polymer melt.
Effect of dyes on moldability of PCA melt was defined by introducing polymer mixture
into molding machine where polymer was melted in nitrogen atmosphere, homogenized with
the dye and then at passing of the melt through spinneret, provided with metal sieves, formed
into PCA monofilament.
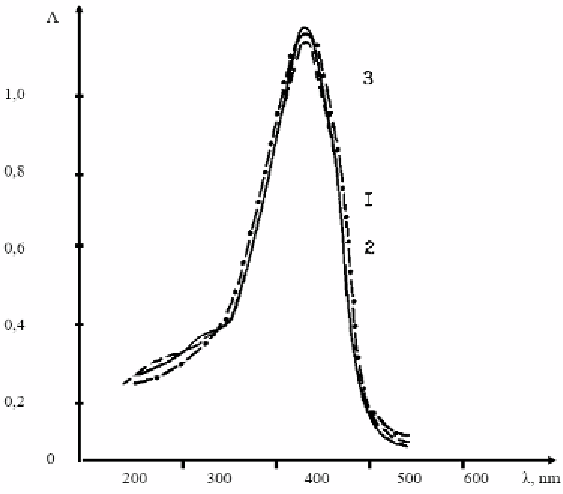
Figure 1.3. Absorption spectra of solutions of the dye XLV - (I) and dyed PCA before the spinneret (2)
and after spinneret (3) in the mixture of formic and trifluoro - acetic acids (1:1).

Search WWH ::

Custom Search