Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
light with the wave length not higher than 400 nm. However, absorption of one quantum of
light not always leads to the formation of one particle of photochemical transformation.
This phenomenon may be caused by a number of reasons. Active molecule may not at all
decay chemically even if absorbed quantum has much more energy than the energy of
dissociation of the strongest molecule. This is probably connected with the fact that energy
absorbed by particular sector of molecule may be distributed along different bonds in
molecule.
The second reason is that initially formed radicals may recombinate faster, than react
with other substances and so excess of energy will be transformed into kinetic energy.
During insolation in natural conditions there takes place weakening of molecular bonds in
amorphous section of polymer.
Insolation in natural conditions and under artifical light source shows that in both cases
change of the value of PETP molecular weight happens less intensively compared with
physico-mechanical properties. Evidently, the fact, that physico-chemical properties are
defined not only by chemical structure, but by complex formations of supermolecular
structure, is characteristics for PETP-fibre.
A great number of investigations were devoted to the problem of oxygen effect on
photodestruction of polyesters. Many researchers consider that the rate of photodestruction
depends on the presence of oxygen [233-235].
Plants, allowing to carry out irradiation both in aerial and airless media [233] are
designed for studying oxygen effect on the rate of photodestruction.
During irradiation in the absence of oxygen the main effects are joints between polymer
chains [234]. Break of the chain and increase of fluorescence are observed in the presence of
oxygen, but there are no lateral joints between chains and only weak decolouration is
observed. Another great difference between photolysis both in the presence and absence of
oxygen is in the quantity of released CO
2
[235].
The important breaking factor for PETP is humidity of air and soil [236]. Besides, the
process of photodestruction is catalyzed by the presence of copper saults [237].
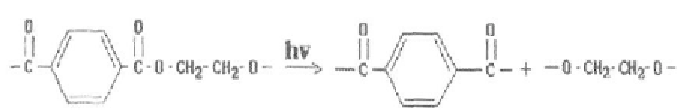
Not excluding the possibility of more complex mechanism of PETP photodestruction and
photooxidation it is supposed that photodestruction of the given polymer takes place
according to the Norrish reaction of I and II type [2].
O
C
O
C O CH CH 0
O
C
O
C
hv
+
O CH CH O
2
2
2
2
Norrisch reaction of I type is the break of the main chain of polymer macromolecule
under the action of ultra-violet light quanta.
According to the Norrish reaction of the II type there occurs intramolecular
separation of the hydrogen atom and formation of the radical with its following decay [238].
Increase of irradiation time causes decline of the properties of PETP-fibre; namely
elogation at rupture and strength. Decrease of strength characteristics and increase of
terephthalic acid content is proportional to irradiation time; hence, according to the quantity
of terephthalic acid one may judge about degree of photodestruction [239]. However,
terephthalic acid, formed as a result of PETP photooxidative destruction, to a considerable





















Search WWH ::

Custom Search