Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
Comparing thermal stability of PVA samples, dyed by active dyes with formation of
chemical bonds and by deactivated dyes , it may be observed that thermal stability of
samples, dyed covalently, is a little higher than PVA containing the same dyes in inactive
form. So, loss of mass for the sample, dyed by the colour LIX during 5 hours is 4,5%; LX -
6%; LXI - 6,7%; LXII - 10,5%.
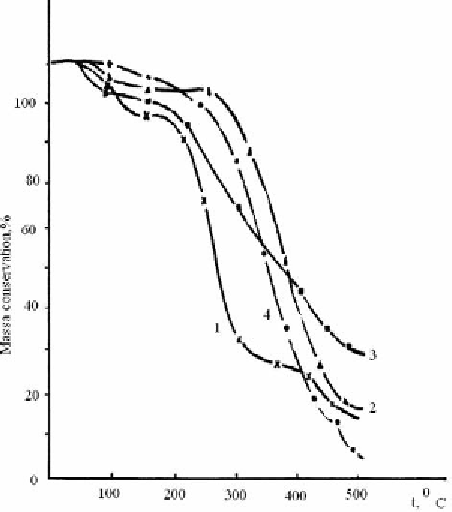
Figure 2.35. Thermal stability of covalently dyed PVA: 1 - undyed, 2 - dyed by LXIII, 3 - dyed by
LXI, 4 - dyed by LIX.
Taking into account the fact that polymer materials must work for a long time in narrow
temperature limits kinetics of thermal decomposition at thermal heating has been investigated.
Data on kinetics of loss of mass at sample heating in the air at 200°C are given in Figure 2.36,
from which it is seen that initial PVA (curve 1) displays the highest loss of mass. So, if
undyed PVA loses about 15% of mass during 5 hours, then the one dyed by the colour LXII -
1,8%.
From Figure 2.37 it is seen that introduction of dyes increases thermal stability of PVA in
the air, moreover it depends not only on the character of the found dye-polymer, but on
chemical structure of the dye itself. So, the highest effect appears in phthalocyanine dyes,
then follow azodyes and antrachinone dyes have the least effect. At the same time general
tendency to improve stability to thermooxidative destruction for samples, containing
covalently linked dyes, is displayed here.

Search WWH ::

Custom Search