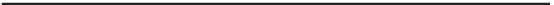Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
for how the other call-management applications support the IPT network. First, let's fol-
low the VoIP flow shown in Figure 2-1.
CME Router
SCCP or SIP
SCCP or SIP
V
Switch
Cisco IP Phone
Cisco IP Phone
Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP)
Figure 2-1
CME Call Flow for On-Network Cisco IP Phones
Essentially, the relationship between CME and the Cisco IP Phones is similar to the rela-
tionship between a mainframe and dumb terminals. CME controls virtually every action
performed at the Cisco IP Phones. For example, if a user picks up the handset, an off-
hook state is sent from the Cisco IP Phone to the CME router using either the Skinny
Client Control Protocol (SCCP) or the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP). We discuss the
differences between these protocols in Chapter 3, but in a nutshell, SCCP and SIP are both
signaling protocols that allow the call-management platform (CME, in this case) to com-
municate with and control an IP Phone. As the user begins to dial digits, each digit is sent
to the CME router (again, via SCCP or SIP). After the user completely dials the phone
number of the other Cisco IP Phone shown in Figure 2-1, CME sends some signaling mes-
sages causing the phone to ring. After the user answers the ringing phone, CME connects
the IP Phones directly and steps out of the communication stream. The phones now com-
municate directly using the Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP), which handles the actual
audio stream between the devices.
Key
To p i c
The fact that CME steps out of the middle of the RTP stream and allows the IP phones to
communicate directly is fantastic because of two primary reasons. First, it eliminates the
CME router as a point of failure. After CME establishes the RTP stream between the IP
phones, it can crash, reboot, or catch fire, and the conversation between the two end-
points continues unhindered (provided the fire did not also burn up the switch). The other
benefit is that the CME router does not become a bottleneck for the RTP stream. If the
links to the CME router became saturated or the router ran out of resources, RTP packets
can drop, causing the call quality to degrade. Keep in mind that we're only talking about
the RTP stream, which contains the audio of the call. All the phone features (such as hold,