Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
DHCP Server
TFTP Server
CME Router
V
1
2
3
4
5
Cisco IP Phone
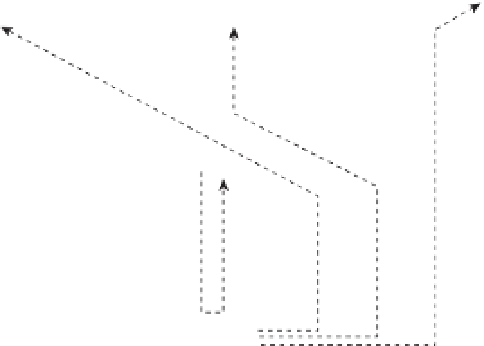
Figure 15-2
Cisco IP Phone Boot Process
3.
The IP phone sends a DHCP request on its voice VLAN. The DHCP server replies
with IP addressing information, including DHCP Option 150, which directs the IP
phone to the TFTP server.
4.
The IP phone contacts the TFTP server and downloads its configuration file and
firmware.
5.
Based on the IP address listed in the configuration file, the IP phone contacts the call
processing server (the CME router, in this case), which supports VoIP functions.
Knowing this boot process virtually plans your troubleshooting process for you! Anytime
a Cisco IP Phone gets stuck in the boot process (for example, it is unable to get a DHCP-
assigned address, reach a TFTP server, or register with the CME router), it reboots itself
and tries again. You can get many clues to how far the phone is getting in the boot process
by carefully watching the messages on the screen. The IP phone tells you when it attempts
to configure a voice VLAN, obtain an IP address, or contact a TFTP server. By watching
the screen, you can identify the step where the phone stops in the boot process and begin
your troubleshooting from that point.
Tip:
Keep in mind that it is normal for a newly installed IP phone to reboot several times
because of firmware and configuration updates.