Database Reference
In-Depth Information
You define the length of time you want the Database Engine Tuning Advisor to run by selecting Limit Tuning
Time and then defining a date and time for the tuning to stop. The longer the Database Engine Tuning Advisor runs,
the better recommendations it should make. You pick the type of physical design structures to be considered for
creation by the Database Engine Tuning Advisor, and you can also set the partitioning strategy so that the Tuning
Advisor knows whether it should consider partitioning the tables and indexes as part of the analysis. Just remember,
partitioning is first and foremost a data management tool, not a performance tuning mechanism. Partitioning may
not necessarily be a desirable outcome if your data and structures don't warrant it. Finally, you can define the physical
design structures that you want left alone within the database. Changing these options will narrow or widen the
choices that the Database Engine Tuning Advisor can make to improve performance.
You can click the Advanced Options button to see even more options, as shown in Figure
10-4
.
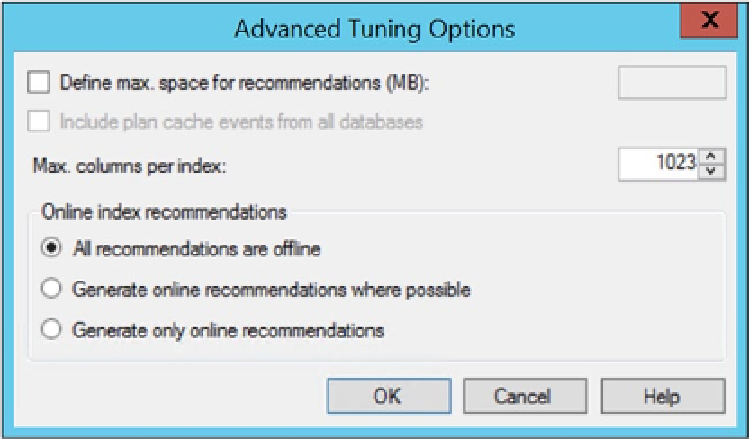
Figure 10-4.
Advanced Tuning Options dialog box
This dialog box allows you to limit the space of the recommendations and the number of columns that can
be included in an index. You decide whether you want to include plan cache events from every database on the
system. Finally, you can define whether the new indexes or changes in indexes are done as an online or offline
index operation.
Once you've appropriately defined all of these settings, you can start the Database Engine Tuning Advisor by
clicking the Start Analysis button. The sessions created are kept in the
msdb
database for any server instance that you
run the Database Engine Tuning Advisor against. It displays details about what is being analyzed and the progress that
made, which you can see in Figure
10-5
.