Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
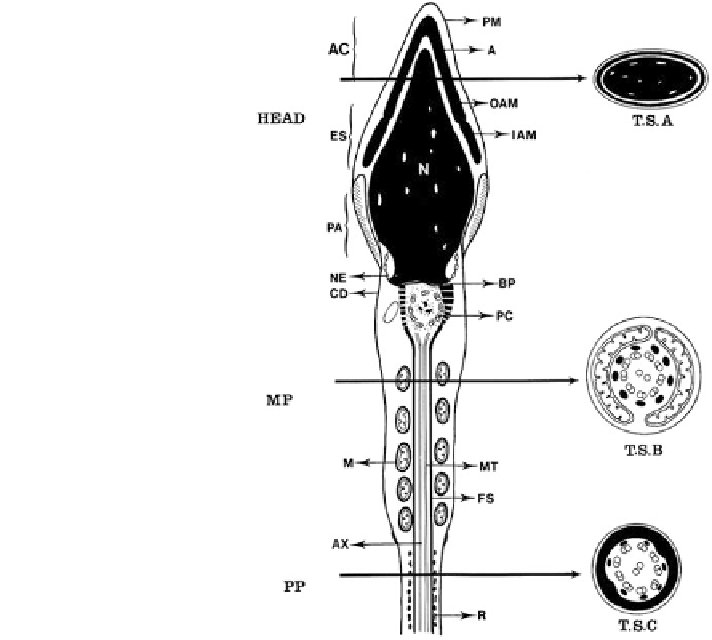
Fig. 5.6 Mature sperm:
ultrastructure—
(Sathananthan
1996
)
A acrosome (black), AC
acrosome cap, AX axoneme,
BP basal plate, CD
cytoplasmic droplet, ES
equatorial segment
Acrosome, FS fibrous sheath,
IAM inner acrosome
membrane, M mitochondria,
MP midpiece, NE nuclear
envelope, OAM outer
acrosome membrane, PA post
acrosomal segment
(fusogenic), PC proximal
centriole, PP principal piece
(tail), R ribs, TS transverse
sections
sperm and is apparently non-functional. The PC retains its typical '9 ? 0' orga-
nization of triplets of MTs presenting the classical pinwheel structure; it is
inherited by the embryo, while the DC is represented by a few disorganized
peripheral MTs with a central doublet extending from the midpiece (MP) axoneme
to the lower limit of the PC (Figs.
5.7
,
5.8
,
5.9
), where it terminates in an accu-
mulation of dense PCM (Sathananthan et al.
1996
,
2001
; Sathananthan
1997
;de
Kretser and Kerr
1994
; Holstein and Roosen-Runge
1981
). For this reason it is
argued that the DC cannot function as a true centriole (Zamboni
1992
; Zamboni
and Stefanini
1970
). The DC is more disorganized cranially and less so caudally
toward the flagellar axoneme in the MP, as revealed in serial transverse sections
(Sathananthan
1996
; Manandhar et al.
2000
). Apart from the centriole, there are
other structures associated with both the PC and DC. The PC is hidden in a vault or
'black box' composed of the capitulum situated immediately beneath the basal
plate and is flanked laterally by nine segmented columns that merge with the nine
outer dense fibers surrounding the MP axoneme and the MT of the DC that are
closely associated with the dense fibers (Figs.
5.6
,
5.7
). For an excellent review of
sperm neck structure see Zamboni (
1992
). The sequence of events in spermio-
genesis and oogenesis is also available on the Web
www.sathembryoart.com
.