Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
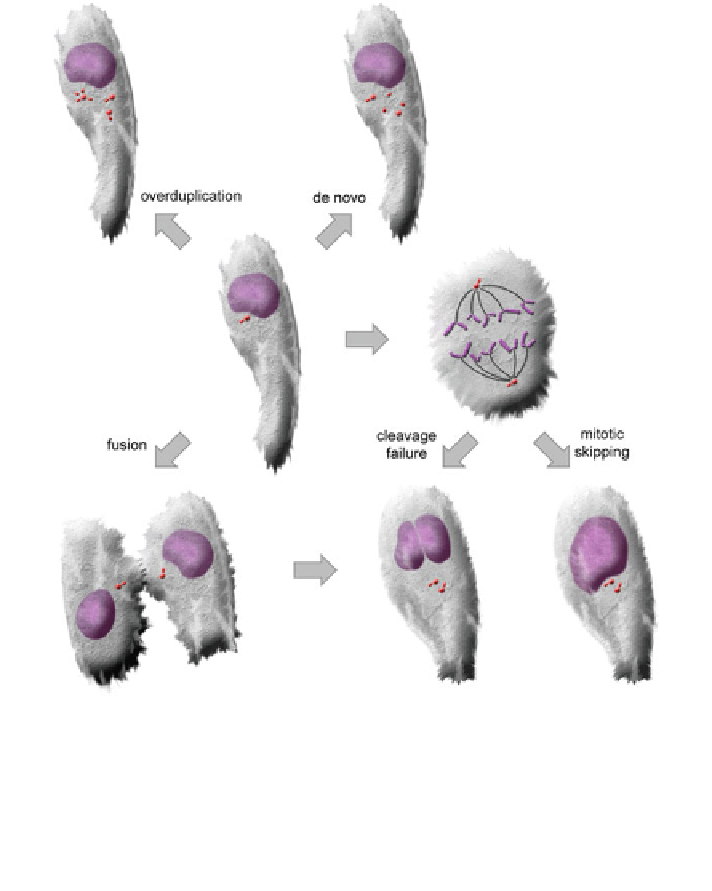
Fig. 17.2 Mechanisms leading to supernumerary centrioles/centrosomes. Centriole overduplication,
and de novo formation results in cells with an undefined number of extra centrioles, whereas cell
fusion, mitotic skipping as well as cleavage failure not only lead to a doubled centrosome number but
also to a duplicated DNA content. In contrast to overduplication, de novo formation, mitotic skipping,
and cleavage failure, cell fusion is not restricted to a defined cell cycle phase. Both overduplication and
de novo centriole formation are assumed to take place during S-phase. Cleavage failure and mitotic
skipping occur in G
2
/M, whereas the first event follows anaphase, the latter is not limited to a specific
mitotic phase (Adopted from Anderhub et al.
2012
)
PLK4 and CPAP to centrioles and thus in the initiation of centriole duplication in
human cells (Cizmecioglu et al.
2010
; Dzhindzhev et al.
2010
; Hatch et al.
2010
)
Abnormalities of diverse tumor suppressors and oncogenes can cause centrosome
amplification (Fukasawa
2007
), which occurs through centrosome over-duplication
during interphase, de novo synthesis of centrosomes or cytokinesis failure (Nigg 2002)
(Fig.
17.2
). Centrosome amplification is frequent in cancer, and is linked to tumori-
genesis and aneuploidy (Nigg
2002
;Lingleetal.
1998
; Pihan et al.
1998
; Neben et al.
2003
;Krämeretal.
2003
; Koutsami et al.
2006
). The extent of centrosomal aberrations