Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
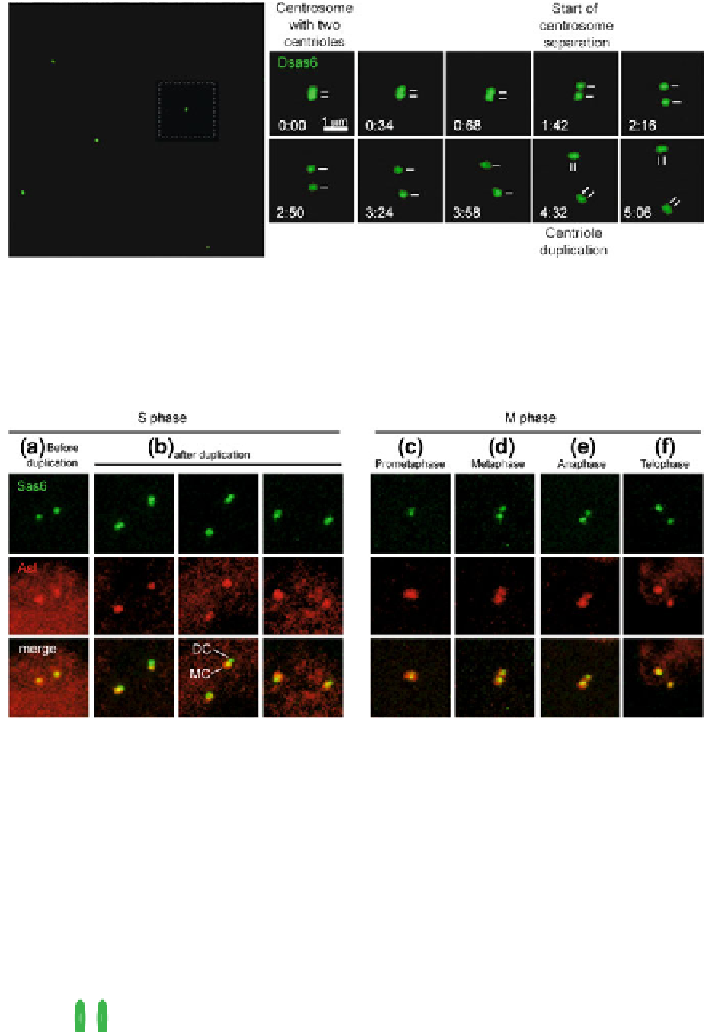
Fig. 1.4 Live imaging of centriole duplication in the early development of an embryo expressing
the centriolar marker Sas-6-GFP. The start of centriole separation marks the splitting of the
centrosome. The left panel shows low magnification of the centrioles, organized in the right
panels by time. The white square in the panel on the right corresponds to the centrioles displayed
in the left panels. A line distinguishes each centriole. S. B produced this picture
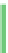
Fig. 1.5 Centriole duplication and centrosome separation in the syncytial blastoderm. The embryo
expressed the centriolar marker Sas-6-GFP (green) and was stained with an anti-Asl antibody; Asl is a
component of the PCM that is found near the centriole (red). a In early S phase, each of the two
centrosomes contain the PCM protein Asl and have a centriole labeled by Sas-6-GFP. b During S phase
each of the centrioles duplicates to form a daughter centriole (Dc). The daughter centriole is marked with
Sas6-GFP but not Asl. c-f Only one of the centriole pairs is shown. The mother and daughter centrioles
start to separate and the daughter centriole accumulates Asl, finally leading to the formation of two
centrosomes. Note that anti-Asl antibody also lightly labeled the nucleus. S. B produced this picture
(a)
(b)
Vertebrate
centrosome
Mother centriole
cross section
Procentriole
cross section
Early fly
embryo centrosome
Early fly embryo
centriole cross section
}
C
}
PCM
Triplet
Microtubules
Doublets
Microtubules
P
CM
B
B
A
A
Mother
centriole
Daughter
Centriole
Mother
centriole
Cartwheel
Procentriole
Fig. 1.6 The fly early embryonic centriole resembles a procentriole. (The fig is modified from
Fig.
1
in (Avidor-Reiss
2010
)