Civil Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
respect to the location of the center of rigidity of the floor. The center of rigidity is the point where the
equivalent lateral story stiffness (for frames or walls) may be considered to be located.
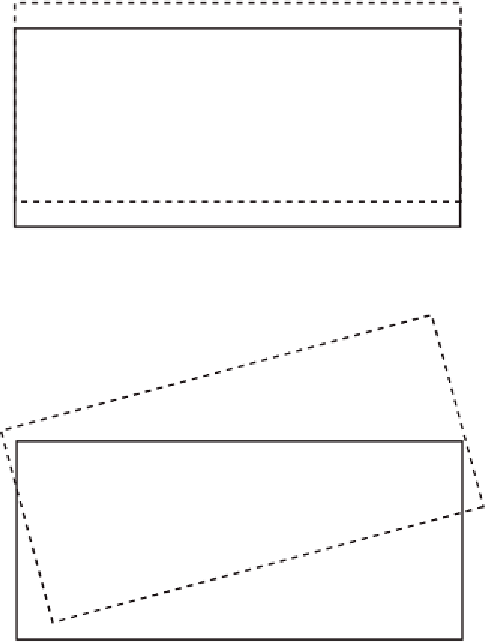
When the centers of mass and rigidity coincide, the lateral load resisting elements in the story displace an equal
distance horizontally (translate) and the story shear V
x
is distributed to the lateral force resisting elements in
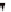
proportion to their relative stiffnesses. If the center of mass does not coincide with the center of rigidity the
lateral load resisting elements in the story displace unequally (translate and rotate) and the story shear V
x
is
distributed to the lateral force resisting elements depending on their location and their relative stiffnesses.
Figure 11-10 illustrates the two cases. ASCE 12.8.4.2 requires that the horizontal force acting on each element
be increased due to accidental torsional moment. Such moment is the result of an assumed offset between the
center of mass and the center of rigidity of the seismic force resisting elements. The assumed offset is
5 percent of the building plan dimension perpendicular to the force direction at each level and is intended to
account for inaccuracies in building weight and stiffness estimate.
CM,CR
V
(a) Centers of mass and rigidity at the same point
M
t
= V
e
CR
CM
e
V
V
(b) Centers of mass and rigidity at distinct points
Figure 11-10 Floor Displacements

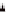




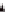

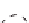













Search WWH ::

Custom Search