Civil Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
American National Standards Institute's ANSI A2-1; ULC-S101 from the Underwriters Laboratories of
Canada; and Uniform Building Code Standard No. 43-1.
10.3.2 ASTM E 119 Test Procedure
A standard fire test is conducted by placing an assembly in a test furnace. Floor and roof specimens are exposed
to controlled fire from beneath, beams from the bottom and sides, walls from one side, and columns from all
sides. The temperature is raised in the furnace over a given period of time in accordance with ASTM E 119
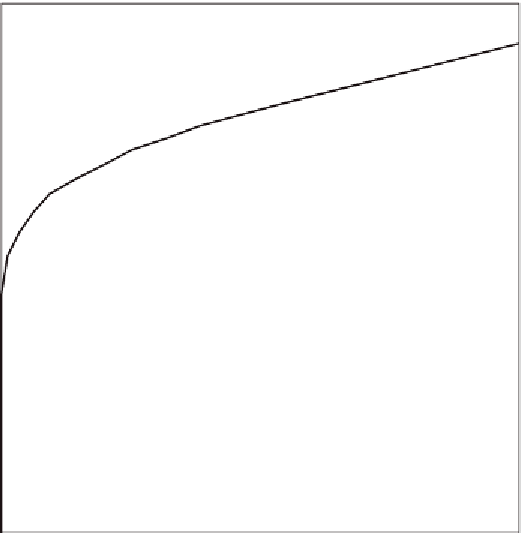
standard time-temperature curve shown in Fig. 10-1.
2500
2000
1600
1000
500
0
0 2 4 6 8
Fire test time, hr.
Figure 10-1 Standard Time-Temperature Relationship of Furnace Atmosphere (ASTM E 119)
This specified time-temperature relationship provides for a furnace temperature of 1000°F at five minutes from
the beginning of the test, 1300°F at 10 minutes, 1700°F at one hour, 1850°F at two hours, and 2000°F at four
hours. The end of the test is reached and the fire endurance of the specimen is established when any one of the
following conditions first occur:
(1) For walls, floors, and roof assemblies the temperature of the unexposed surface rises an average of 150°F
above its initial temperature of 325°F at any location. In addition, walls achieving a rating classification of
one hour or greater must withstand the impact, erosion and cooling effects of a hose steam test.
(2) Cotton waste placed on the unexposed side of a wall, floor, or roof system is ignited through cracks or
fissures developed in the specimen.








Search WWH ::

Custom Search