Civil Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
4.4.1
Shear in Flat Plate and Flat Slab Floor Systems
Two types of shear need to be considered in the design of flat plates or flat slabs supported directly on columns.
The first is the familiar one-way or beam-type shear, which may be critical in long narrow slabs. Analysis for
beam shear considers the slab to act as a wide beam spanning between the columns. The critical section is
taken a distance d from the face of the column. Design against beam shear consists of checking the
requirement indicated in Fig. 4-12(a). Beam shear in slabs is seldom a critical factor in design, as the shear
force is usually well below the shear capacity of the concrete.
Two-way or “punching” shear is generally the more critical of the two types of shear in slab systems supported
directly on columns. Punching shear considers failure along the surface of a truncated cone or inverted pyramid
around a column. The critical section is taken perpendicular to the slab at a distance d/2 from the perimeter of
a column. The shear force V
u
to be resisted can be easily calculated as the total factored load on the area
bounded by panel centerlines around the column, less the load applied within the area defined by the critical
shear perimeter (see Fig. 4-11). In the absence of a significant moment transfer from the slab to the column,
design against punching shear consists of ensuring that the requirement in Fig. 4-12(b) is satisfied. Figures 4-13
through 4-15 can be used to determine
φ
V
c
for interior, edge and corner columns, respectively.
C
L
panels
˜
1
V
u
≤φ
V
c
≤φ
C
ritical
section
2
f
c
2
d
ʹ
≤
0.095
2
d(
f
c
=
ʹ
4000psi)
d
where V
u
is factored shear force (total factored load on
shaded area). V
u
is in kips and ˜
2
and d are in inches.
(a) Beam shear
V
u
≤φV
c
where :
˜
1
C
L
panels
⎧
⎛
⎜
4
β
⎞
⎟ ʹ
⎛
⎜
4
β
c
⎞
⎟
⎪
⎪
⎪
φ 2 +
f
c
b
o
d = 0.048 2 +
b
o
d
Critical
section
⎛
⎜
⎞
⎟
ʹ
⎛
⎜
⎞
⎟
φ
α
s
d
0.048
α
s
d
φ
V
c
=
least of
⎨
b
o
+
2
f
c
b
o
d
=
b
o
+
2
b
o
d
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
d/2
φ4
f
c
b
o
d = 0.19b
o
d
ʹ
⎩
V
u
= factored shear force (total factored load on shaded area), kips
b
o
= perimeter of critical section, in.
β
(b) Two-way shear
= long side/short side of reaction area
α
s
= constant (ACI 11.11.2.1 (b))
Figure 4-12 Direct Shear at an Interior Slab-Column Support (for normal weight concrete and
›
= 4000 psi)







































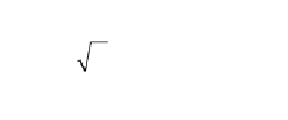






















Search WWH ::

Custom Search