Civil Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
4.3
TWO-WAY SLAB ANALYSIS BY COEFFICIENTS—DIRECT DESIGN METHOD
For gravity loads, ACI Chapter 13 provides two analysis methods for two-way slab systems: the Direct Design
Method (ACI 13.6) and the Equivalent Frame Method (ACI 13.7). The Equivalent Frame Method, using
member stiffnesses and complex analytical procedures, is not suitable for hand calculations. Only the Direct
Design Method, using moment coefficients, will be presented in this Chapter.
The Direct Design Method applies when all of the conditions illustrated in Fig. 4-5 are satisfied (ACI 13.6.1):
There must be three or more continuous spans in each direction.
Slab panels must be rectangular with a ratio of longer to shorter span (c/c of supports) not greater than 2.
Successive span lengths (c/c of supports) in each direction must not differ by more than one-third of the
longer span.
Columns must not be offset more than 10% of the span (in direction of offset) from either axis between
centerlines of successive columns.
Loads must be due to gravity only and must be uniformly distributed over the entire panel.
The unfactored live load must not be more than 2 times the unfactored dead load (L/D
≤
2).
For two-way slabs, relative stiffnesses of beams in two perpendicular directions must satisfy the minimum
and maximum requirements given in ACI 13.6.1.6.
Redistribution of moments by ACI 8.4 must not be permitted.
Uniformly Distributed Loading (L/D ≤ 2)
(
≥
2/3)
˜
1
˜
1
˜
1
Three or More Spans
Rectangular slab
panels (2 or less: 1)
˜
2
Column offset
≤
˜
2
/10
Figure 4-5 Conditions for Analysis by the Direct Design Method
























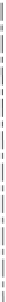
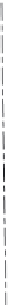











































Search WWH ::

Custom Search