Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 4.3
Source of data for Figs.
4.6
and
4.7
Symbol
Source
Aerofoil
Re
1.6 9 10
5
+
Fage and Johansen [
12
]
Flat plate
10
5
9
Kogaki et al. [
5
]
MEL 081
10
5
*
Bruining [
15
]
Cambered flat plate
6 9 10
4
r
Bruining [
15
]
Cambered flat plate
5.1 9 10
4
O
Zhou et al. [
11
]
NACA 0012
1.05 9 10
4
Zhou et al. [
11
]
NACA 0012
5.3 9 10
3
h
Zhou et al. [
11
]
NACA 0012
Fig. 4.6 a High-angle lift
coefficient for Reynolds
numbers below 2 9 10
5
.
b High-angle drag coefficient
for Reynolds numbers below
2 9 10
5
. Data sources listed
in Table
4.3
(a)
1.4
1.2
1
C
l
= 2sin cos
α
α
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
angle of attack (
°
)
(b)
2
1.5
C
d
= 2sin
2
1
α
0.5
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
angle of attack (
°
)
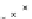
4.5 The Circulation
Section 3.4
considered the two-dimensional analogue of the axisymmetric blade
elements at radius r. This analogue is sketched in Fig.
4.8
, where only four of the
infinite cascade of aerofoils (up and down the page) is shown. In terms of the blade
element chord, c, the non-dimensional spacing between the elements is just the
inverse of the solidity, r, defined by Eq.
3.14
. Now assume for simplicity that the
























































































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search