Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
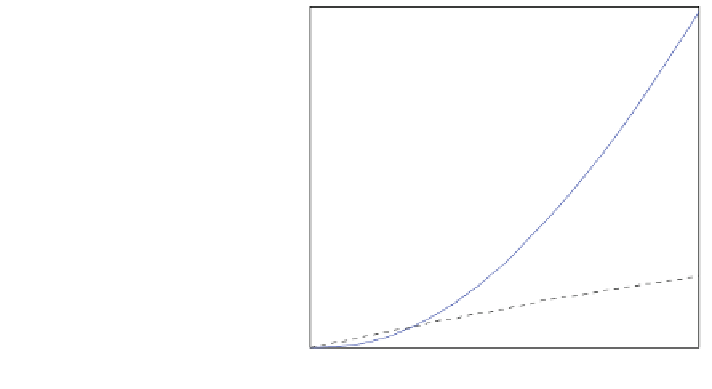
Fig. 7.1 Characteristics of
the Ginlong 500 A permanent
magnet generator, with rated
conditions and optimum
power trajectory for design
example
900
Power (W)
Torque x10 (Nm)
Efficiency x10 (%)
800
7
54 W
700
600
550 rpm
500
Power = 754(
Ω
/550)
3
400
300
200
100
0
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
Generator speed (rpm)
power is produced at wind speeds above the average for the particular site. If the
average is 5 m/s—a good value for small turbines—then no reduction in power
due to control actions, or through braking or furling, should occur at less than
about 10 m/s. For the remaining discussion of rated wind speed, it is assumed that
the power curve stays flat at the desired rated power above the rated speed.
Obviously, for constant rated power, lowering the rated speed will produce more
power on average. However this usually requires increasing the blade radius and
cost. X must remain constant to maintain power for a particular generator, see
Fig.
7.1
,sok must increase and will soon exceed the range for optimum perfor-
mance as seen in
Chap. 5
. Thus a choice of around 10 m/s is a compromise, but a
reasonably common and often very sensible one. Note that rated aerodynamic
torque is not changed by a change in rated wind speed so the starting issues,
exemplified by the ratio of starting to rated torque are not strongly influenced by
the choice of rated wind speed.
Table
7.1
lists the turbine parameters for the optimisation. Those shown bold
are set by the choice of generator which has a maximum cogging torque
of 0.5 Nm.
3
The case of no cogging torque will be studied for comparison.
Furthermore, it is assumed that the hub radius is the outer radius of the gen-
erator. The blade radius, tip speed ratio, and maximum power are now dis-
cussed in terms of Fig.
7.1
. The choice of maximum power as being close to
the maximum available from the generator is obviously important in reducing
cost, but also the higher the power, the lower the ratio of cogging to rated
torque. However, the generator's maximum power should be greater than the
maximum design power of the turbine, for safety and to allow some leeway for
the control system.
For
the Ginlong
generator a
rated
power of 754 W
at
3
Note that the author's measurements of two of these generators gave Q
R
= 0.35 Nm, see
Table
1.8
.























































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search