Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
6
LAG PERIOD
5
4
3
2
a
Turbidity
Sp. Conductivity
Chl-
1
0
123456789101112131415161718192021222324
Time (days)
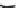
Figure 2.10
Fluorimetric monitoring of lake water parameters. Fluorimetric traces of mean lake water chlorophyll-
a
concentration and turbidity (both arbitrary units) obtained over a 24-day period (August 15-September 7, 2006) from
the remote-sensing buoy shown in Fig. 2.9. Values were recorded at mid-day, depth 1 m. The decrease in chlorophyll-
a
corresponds to a decline in live algal biomass, with a lag period before the related decline in phytoplankton turbidity
due to persistence of dead cells (no chlorophyll) in the water column. No significant change occurs in the mean specific
conductivity. Fluorimeter parameters are given in Table 2.1 and text.
contribute to the pigment assessment of algal
biomass. Normally this effect would be minimal.
On-site measurement of chlorophyll
concentrations
Chlorophyll pigments may degrade to phaeo-
phytin products, which are relatively stable and
which interfere with fluorimetric or spectrophoto-
metric determination of chlorophyll. This degra-
dation can be compensated for, however, since
phaeophytin concentrations can be estimated sep-
arately on the same samples from which the
chlorophyll was determined (Wetzel and Likens,
1991).
This can be carried out using fluorimeter probes or
by colorimetric analysis.
Fluorimeter probes
Fluorimeters measure the
intensity and the wavelength distribution of light
emitted as fluorescence from molecules that are
excited at specific wavelengths. Using different exci-
tation wavelengths and collecting light at different
wavelength emissions (Table 2.1), they can be used
to measure aquatic concentrations of chlorophyll-
a
(index of total phytoplankton biomass) and other
algal pigments (assessment of different algal groups)
within the water column.
Techniques for the determination of chlorophyll
-a
concentration have been described in various stan-
dard texts (Wetzel and Likens, 1990; Eaton et al.,
2005) and involve either direct on-site (lake water)
measurement or subsequent analysis of aquatic sam-
ples back in the laboratory.
Total chlorophyll
Fluorimeter probes can be used
for direct readings by manually lowering into the

























































































































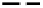










Search WWH ::

Custom Search