Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
s
f
e
20 μm
20 μm
Figure 4.51b
Phacus
. Typical flattened pear-shaped
cell with a single emergent flagellum (f), a red eyespot
(e), a rigid pellicle covered in spines (s) and an elon-
gate posterior tail. Reproduced with permission from R.
Matthews.
Figure 4.51a
Mallomonas
. Single motile cell (flagel-
lum not visible) showing a surface covering of silica
scales, many of which bear elongate trailing bristles.
Reproduced with permission from R. Matthews.
overlapping plates made of silica. These
plates (which may not be obvious in
live material) bear spines so that the
whole organism is covered with these long
spines. The spines may become detached
from the plates, especially on preserva-
tion. There are two golden-brown parietal
chloroplasts. The food reserve is leucosin.
Common in the plankton of standing
waters.
Mallomonas
can impart unwanted
odours to drinking water (Palmer, 1962).
Chrysophyta. Plate XV, Fig. 4.51a.
(b) Cells without spine-bearing scales
.................................
108
15 μm
108
(107) (a) Cells with one, two or four flagella
attached at one end only . ...........
109
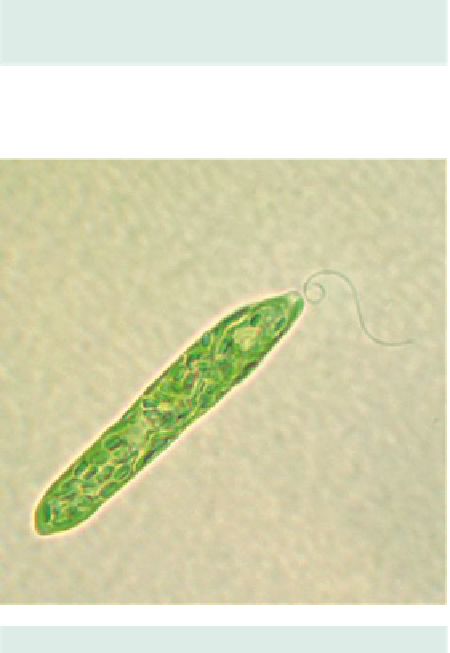
Figure 4.51c
Euglena.
Single cell with discoid chloro-
plasts and prominent apical flagellum.
(b) Cells with two flagella attached other
thanatanteriorend................
123
NB.
In dinoflagellates two flagella arise at
the centre of the cell. One trails backwards





Search WWH ::

Custom Search