Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
h
10 μm
a
h
10 μm
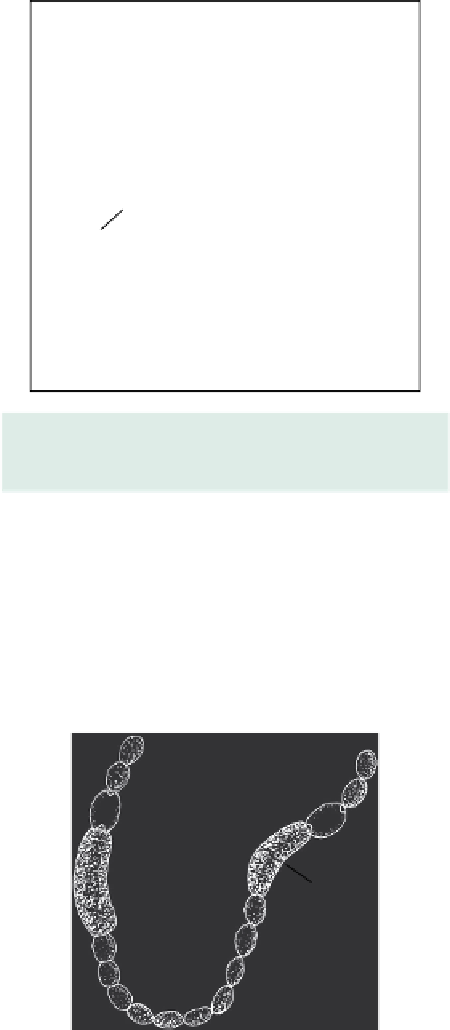
Figure 4.24b
Anabaena circinalis.
Filament with
spherical vegetative cells and akinetes (a) not adjacent
to heterocysts (h).
50 μm
the edge. Akinetes may occur in older parts
of the colony and are produced between
heterocysts (unlike
Anabaena
). Hormogonia
may be occasionally produced. The cells are
approximately spherical to barrel-shaped 3-
6 μm wide. Grows on damp or wet surfaces,
shallow waters. Can be free-floating or
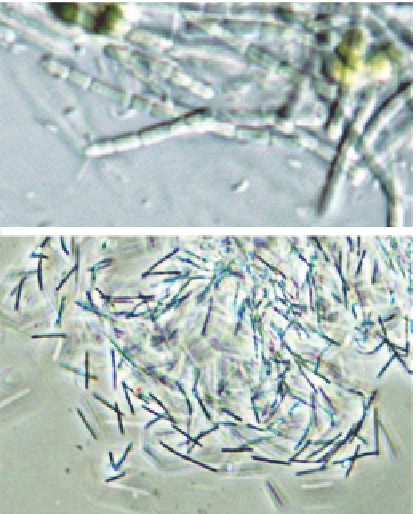
Figure 4.24d
Pseudanabaena.
Top: Details of single
filaments, with cylindrical cells deeply constricted at
cross walls. Bottom: Edge of colony, showing numerous
dispersed short filaments. Reproduced with permission
from R. Matthews.
attached. It occurs in rice paddies where
it is used to contribute nitrogen to the
rice crop.
Nostoc
can produce toxins in
freshwaters, for example, microcystins and
lipopolysaccharides (Chorus and Bartrum,
1999). Cyanophyta. Fig. 4.25.
h
a
The genus
Pseudanabaena
comprises a vari-
ety of forms with various common fea-
tures, including short trichomes capable of
motility. Cells are spherical, barrel-shaped
or cylindrical with trichomes markedly
constricted at the cross-walls. Widespread
amongst other algae in ponds and lake mar-
gins. Fig. 4.24d.
10 μm
Figure 4.24c
Anabaena flos-aquae.
. Single filament
with sausage-shaped akinetes (a) adjacent to heterocysts
(h).
53
(46) (a) Trichomes form a regularly spirally
coiled cylinder in which the individual cells
may be difficult to distinguish . . .
Spirulina









Search WWH ::

Custom Search