Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
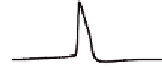
Figure 2. Interaction of several parameters makes unpredictable the spiking mode between dendrites
(thin) and axon/soma (thick traces). A. Cross-analysis of inhibition, excitatory input and dendritic po-
tassium conductance. B. Cross-analysis of inhibition, excitatory input location and dendritic potassium
conductance. Note that for a fixed value in any one variable, the spiking mode can be totally different
upon changes in third variables. N: no firing; Ax: axon fires first (backpropagation); D: dendrite first
(full forward); ps: pseudosaltatory forward; d: aborted dendritic spike; =: simultaneous axo-dendritic
firing. D-M: dendrite fires first and is followed by multiple firing. Ax-M: axon-first and multiple firing.
Modified from Ibarz et al., 2006.
A
G A B A
A
= G lu
G A B A
A
= 2 0 % G lu
2 7 0
N
Ax
N
(ps)
d
2 1 0
(ps)
D
D
D-M
1 5 0
1 0
3 0
7 0
1 0
3 0
7 0
B
2 m s
D is ta l
in p u t
M id d le in p u t
4 0 0
N
d
D
N
1 0 0
D
=
(ps)
Ax
D-M
2 0
Ax-M
1 0
3 0
7 0
1 0
3 0
7 0
T o ita l e x c ita to ry c o n d u c ita n c e (n S )
Small Dendrites Talking To Parent
Dendrites
number varied enormously depending upon the
different conditions. The difference between con-
ditions promoting full-forward, pseudosaltatory,
or backward propagation between apical shaft and
the axon were neither simple nor obvious. The
number of local spikes and the temporal scattering
constituted the best predictive element for both
cell output and the mode of dendrite-to-axon fir-
ing. As many as 6-10 lateral spikes (out of a total
of 27 possible in our model) were sufficient to
produce a cell output under most initial conditions
and input locations. Temporal scattering between
local spikes ≤ 1 ms was observed for input pat-
The different firing modes mentioned above to
classify the dendritic apical shaft-to-axon coupling
are derived from the variations in the spatiotem-
poral distribution of firing branches within the
overall dendritic structure.
We examined this pat-
tern in order to gain insight of local integration,
and the relationship between spiking on secondary
branches and the main shaft. A small number of
synaptically activated local spikes was sufficient
to initiate a forward spike, although the minimum



































Search WWH ::

Custom Search