Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
ing motor neurons, respectively, with the shared
resources signifying that two motor neurons are
interconnected. The exchange of
r
i
(or
r
j
) resources
between two nodes results in pre-defined firing
frequencies of two motor neurons.
The representative cases of three gait patterns
of a cockroach, i.e., metachronal, medium-speed,
and fast-speed locomotions, according to the
prototypes of Collins and Stewart (1993b), are
analysed by using the discrete OBBs. A transition
between different gait patterns is usually mediated
by command signals from CNS under a conscious
reflex, or a population of neurons in CPG in direct
response to external stimuli under an unconscious
reflex. Either case involves modulation of the con-
nection topology and internal parameters of CPG
building blocks which can greatly alter network
operations (Getting, 1989).
Figure 3 shows a conceptual hexapod's CPG
representing gait phase relationship
between six
legs. Each leg is simplified as having one degree
of freedom with a pair of flexor and extensor mo-
tor neurons and muscles, though any degrees of
freedom
of
a leg are feasible by assuming more
complexity under the proposed strategy. From an
anatomical point of view, cockroach leg movement
is driven by flexor and extensor motor neurons.
Flexor muscles lift a leg from the ground, while
extensor muscles do
the opposite. This procedure
can be well imitated by an OBB module by taking
neurons
i
and
j
in the module as flexor
and extensor
motor neurons, respectively
(see Figure 4).
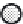
Figure 3. Movement circulation sequences and phase relations among six legs of a cockroach, each
leg represented by one electrically compact node. White colour means legs on the ground, extensor
neurons and muscles activity; black colour means legs swing, flexor neurons and muscles activity. (a)
Metachronal gait. (b) Medium-speed gait. (c) Fast-speed gait.
L1
L2
L3
R1
R2
R3
a
0
1/6
2/6
3/6
4/6
5/6
L1
L2
L3
R1
R2
R3
b
0
1/4
2/4
3/4
L1
L2
L3
R1
R2
R3
c
1/2
0




























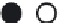








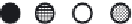























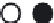





























































Search WWH ::

Custom Search