Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
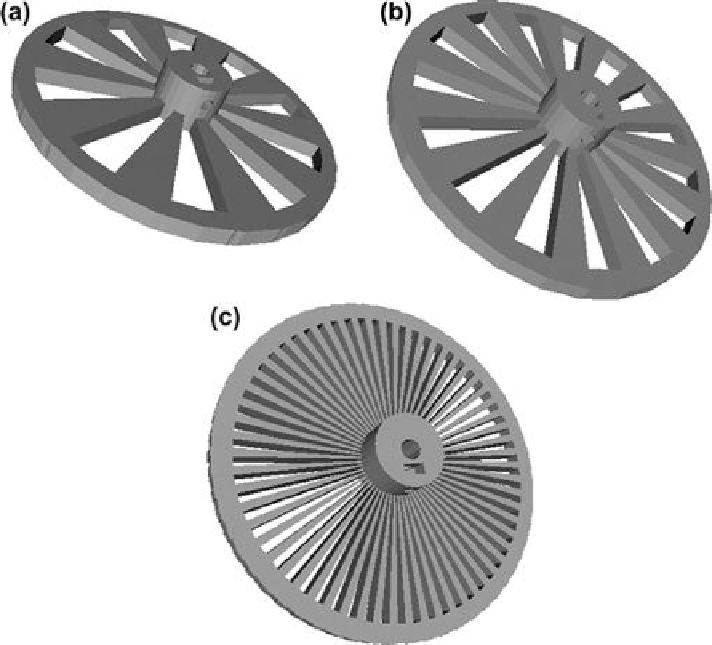
FIGURE 6.3
Rendered parametric design in OpenSCAD on an open-source optical chopper
wheel with (a) 10 slots, (b) 15 slots and (c) 60 slots.
6.1.2 Open-source 3-D printers
which as shown in
Chapter 5
can be constructed for <$600, have made the cost of rapid pro-
ating nature (approximately 50% of its own parts can be self-printed) makes it an extremely
useful platform for open-source fabrication and maintenance of laboratory equipment. The
printing process for the additive layer manufacture of scientific experimental components dis-
cussed in this chapter is a sequential layer deposition. The RepRap extruder intakes a ilament
of the working material, then the Z (vertical) axis will raise, and the extruder will deposit an-
other layer on top of the first. In this way, it can build three-dimensional models from a series
of two-dimensional layers [
3
]
.
Figure 6.4(a)
shows the detail of a RepRap printing out a com-
shows another component of the same filter wheel printing, and also displays the assembly
Search WWH ::

Custom Search